NIS2 (Network and Information Security 2) is an EU-wide cybersecurity directive that applies to information systems, computer networks, applications, software, and data. Its purpose is to strengthen organizational resilience against cyberattacks. It introduces mandatory measures to raise the overall cybersecurity maturity of organizations operating within EU member states.
If your company falls under NIS2, you must comply with requirements related to secure processes, employee training, system and network protection, IT infrastructure, and data security.
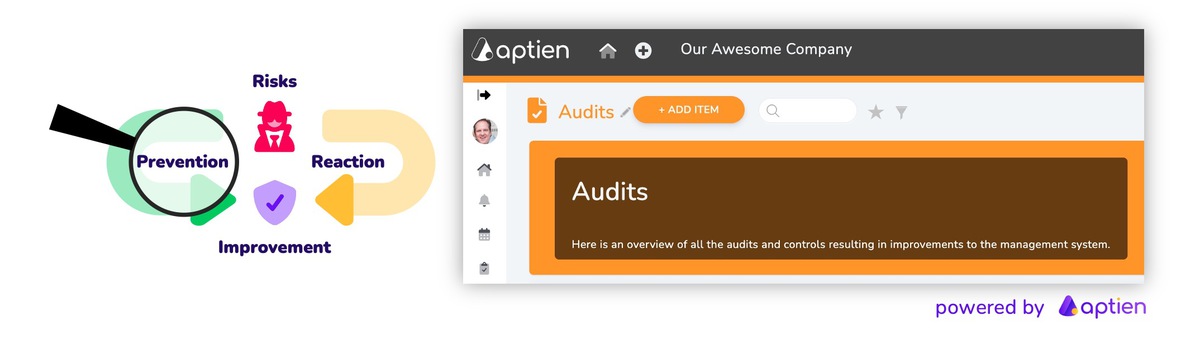
What Does Your Company Need to do if it’s Subject to NIS2?
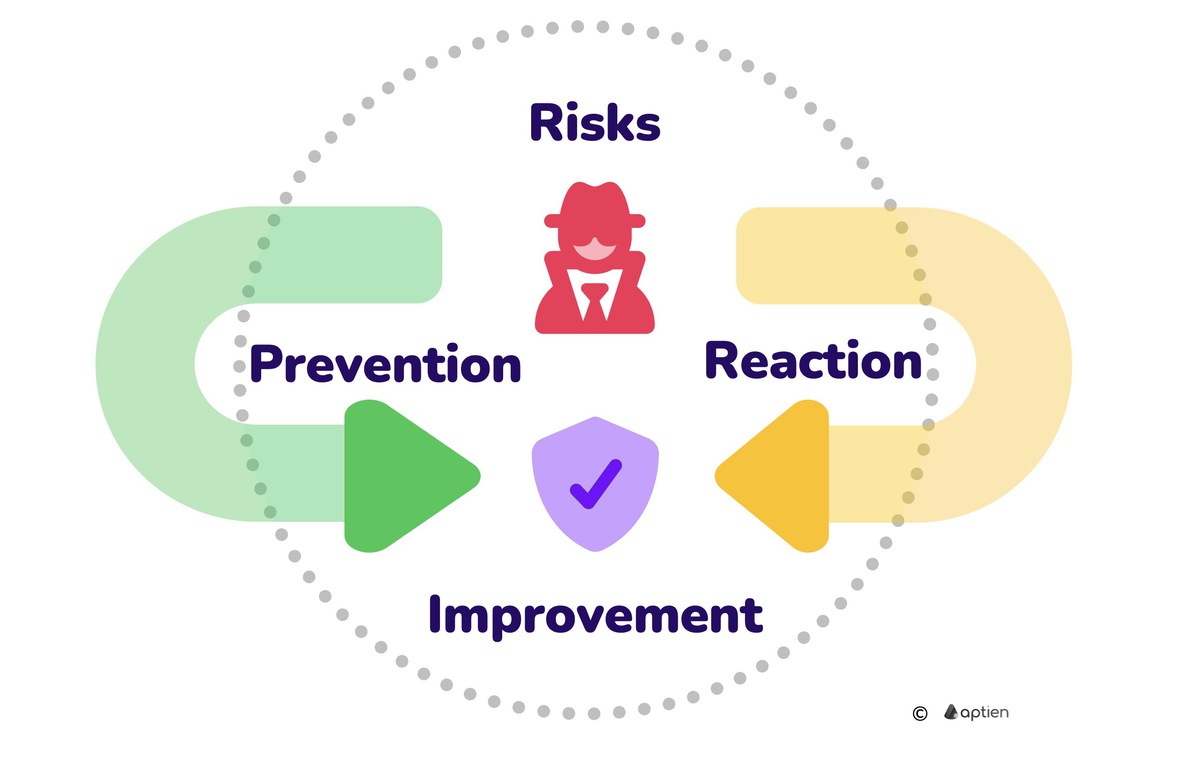
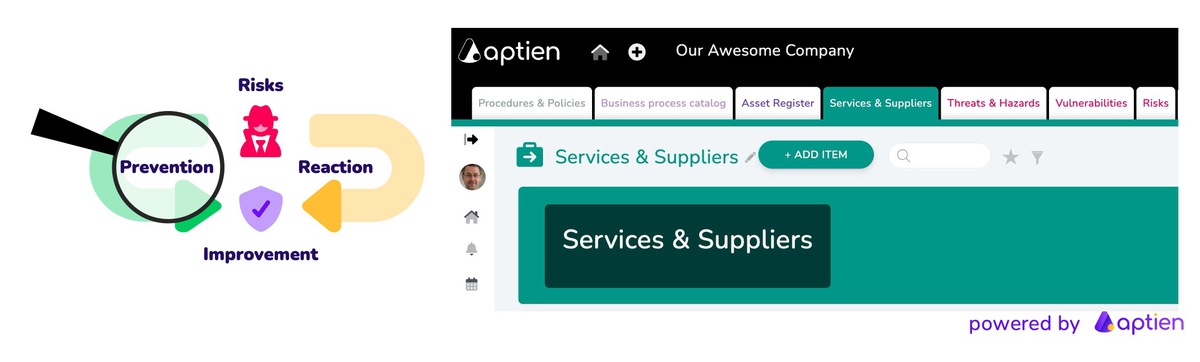
Under the Cybersecurity Act and NIS2, your organization is essentially required to:
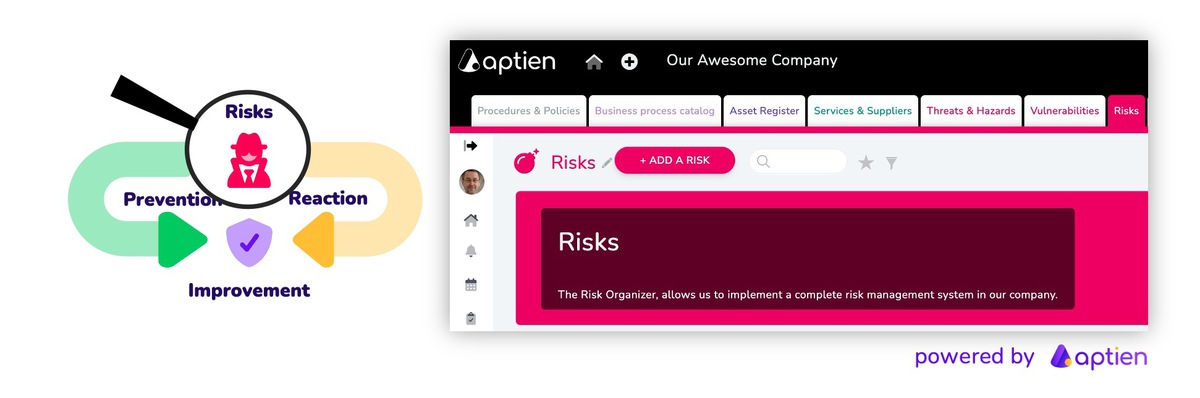
- Know your risks: identify threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts — understand what could go wrong
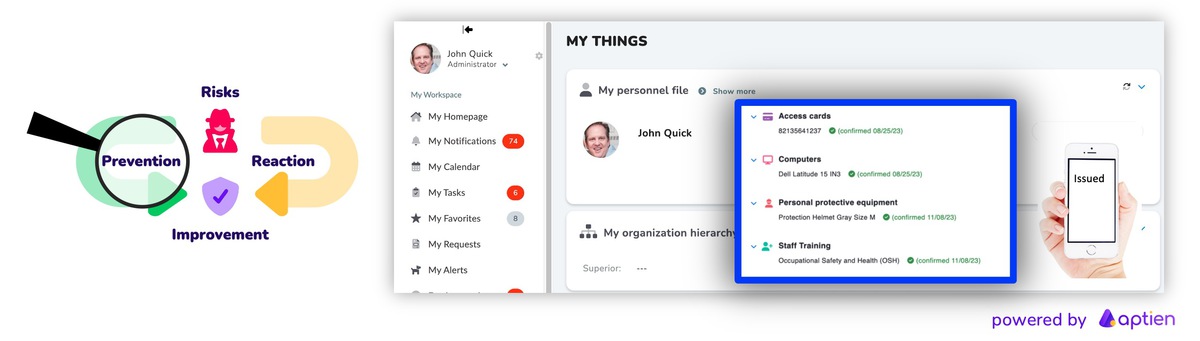
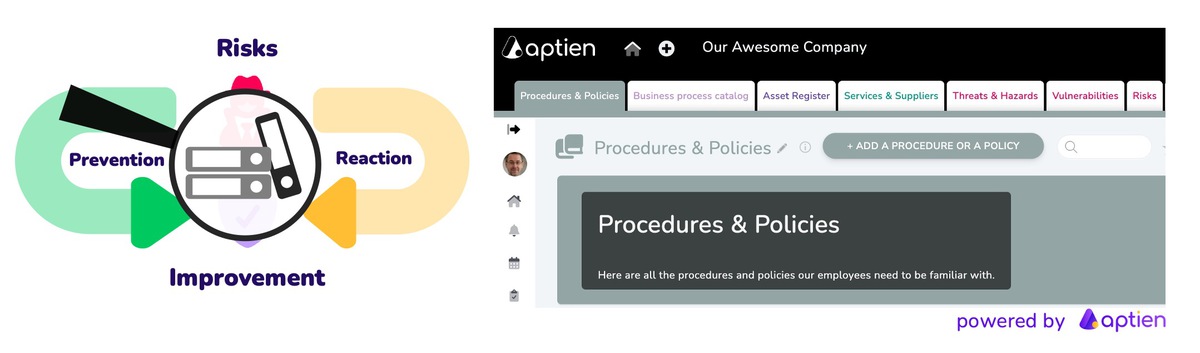
- Prevent issues: implement appropriate controls and safeguards to reduce risk
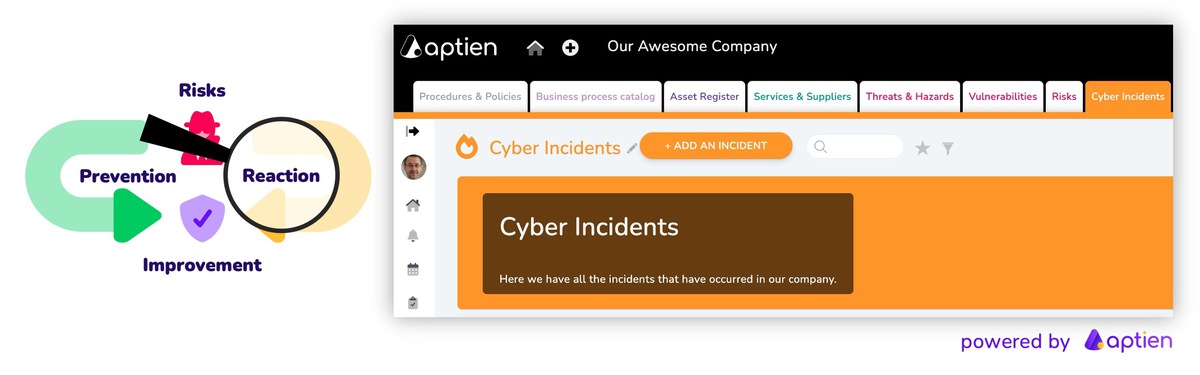
- Respond effectively: be prepared for incidents, including detection, response, and mandatory reporting
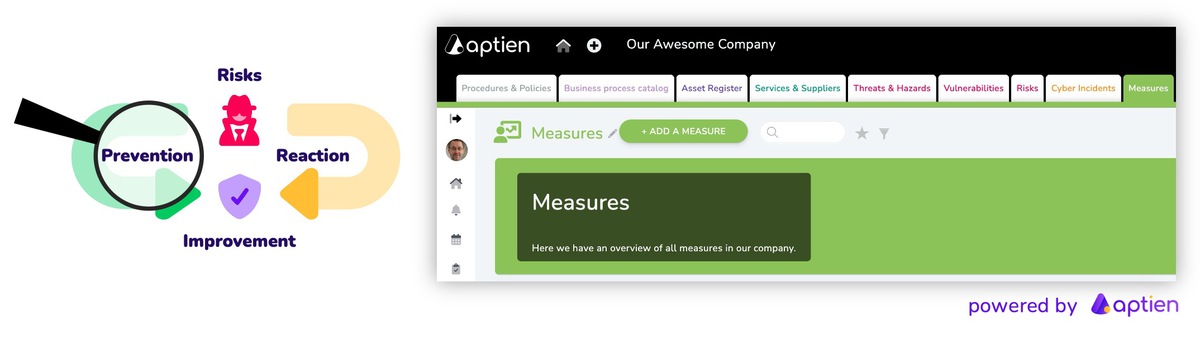
- Continuously improve: ensure management accountability and regularly reassess risks and controls
NIS2 Compliance: Which Organizations Are Affected
Who Is Responsible for NIS2 and What Are the Penalties for Non-Compliance?
- The directive introduces direct accountability for executive and board members, who must ensure that required cybersecurity measures are implemented and maintained.
- Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, including fines of up to EUR 10 million or 2% of annual global revenue, whichever is higher.
- Each EU member state determines the exact way the directive is implemented into national law, so specific obligations and enforcement details may vary by country.
What NIS2 Means for Companies and Organizations — and What Obligations It Brings
In practice, NIS2 requires organizations to implement appropriate, fit-for-purpose, and proportionate technical, process, management, and organizational controls. The key principle is proportionality: NIS2 does not require every company to encrypt everything or invest in the most advanced technologies. Instead, measures must be appropriate to the company’s size, budget, and the value and sensitivity of its data.
Specific obligations differ for organizations classified as “essential” (higher requirements) and “important” (lower requirements), but the overall objective remains the same: to reduce the risk of cyberattacks, data breaches, theft, loss, or operational disruption.
Below is an overview of what these obligations typically include. Many SMBs may already comply with parts of NIS2 — they often simply need to formalize, document, and standardize what they are already doing.
How we Help you Meet NIS2 Requirements
Aptien makes it easier to meet a large portion of your compliance obligations in one place. It supports risk management, complete compliance documentation, asset inventory, incident tracking, and managing corrective and preventive actions stemming from audits, risk assessments, or specific incidents. Aptien works as an integrated risk and compliance management system in a single environment.
What Your Company Needs to Do: Ten Key Steps
- Identify your risks, assets, systems, and third-party vendors
- Establish risk management and define executive ownership and accountability
- Protect data and information and control access to it
- Reduce human error through employee training and a strong security culture
- Secure your IT and information systems—applications, software, hardware, and other IT equipment
- Manage outsourced IT services and their providers
- Protect against cyberattacks and be able to detect, respond to, and report incidents
- Ensure business continuity and disaster recovery for operations and processes after an attack or outage
- Implement necessary policies and procedures
- Maintain ongoing operations and continuously improve the program above
1. Know Your Risks, Assets, Systems, and Vendors Means:
- maintaining documentation on your assets — data, information, and IT equipment
- identifying which data is critical for business operations
- documenting business and IT risks
- understanding what else must stay operational for the business to run
- establishing a regular risk assessment process
- defining how each risk will be addressed and mitigated
- tracking your supporting assets, IT equipment and infrastructure
- keeping an inventory of purchased IT services and their vendors
- maintaining documentation on backups, testing plans, and maintenance
2. Implementing Risk Management and Accountability in Your Company Means:
- maintaining a risk organizer in line with cybersecurity legal and regulatory requirements
- keeping an inventory of primary and supporting assets and their relationships
- defining roles and responsibilities for cybersecurity
- establishing the necessary policies and procedures
3. Manage Access to Information, Assets, and Security
- know who has access to what and why (who holds which physical keys or access cards)
- manage employee permissions and access rights
- digitally issue and track keys and access cards for employees using a simple app
- maintain your process documentation for information security management
- during employee onboarding, control who gets which permissions and why, who knows which passwords, and who has physical access at the company (keys, access cards)
- during employee offboarding, revoke their access and permissions
4. Reducing Human Error Through Employee Security Awareness and Training
Effective NIS2 compliance requires ongoing employee education to minimize human-related risks. This includes:
- establishing structured employee training and development plans
- tracking who has been trained, when the training occurred, and which topics were covered
- digitally onboarding employees to security policies and required documentation
- continuously educating staff about common types of cyberattacks and social engineering threats
- regularly training employees to understand the sensitivity of the data they handle and the risks associated with it
- conducting ongoing training on password hygiene, authentication practices, and secure use of login credentials
5. Ensuring the Security of Software, Hardware, and IT Infrastructure
This includes:
- implementing data protection measures such as backups, encryption, or other safeguards
- controlling who has access to data and information
- securing your information systems, applications, and software
- protecting your company network from attacks (e.g., using a firewall and a secure gateway)
- purchasing and operating secure technologies
- performing regular maintenance
- applying updates and patches on a regular basis
- enabling monitoring for cyber threats
- avoiding insecure practices such as sharing your Wi-Fi password
- implementing detection and evaluation of various attacks, viruses, malware, and other cyber threats (preventive measures)
- ensuring the physical security of your IT infrastructure
- keeping facilities physically secured (e.g., locks, access control, camera systems)
6. Managing IT Service Providers
This means:
- having a clear overview of all your IT service providers, including cloud services
- ensuring they are properly vetted and that contracts address security requirements
- knowing what data you store with each provider
- ensuring no unauthorized external party can access your data
- maintaining documentation on the security of all applications and software you use
- keeping records of service providers and their access rights
- keeping records of the security measures used by third-party services you rely on
7. Recording and Managing Security Incidents
Under NIS2, this means:
- recording cyberattacks, data loss, credential loss, and any other security incidents that affect the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of your systems or data
- documenting incidents and ensuring they are properly handled, including response, analysis, and follow-up
- being able to mitigate and manage the impact of security incidents
- being able to notify affected customers or users when required
National Implementation Differences
- Because NIS2 is an EU directive, each member state must transpose it into national law. This means that specific requirements, procedures, reporting rules, and penalties may differ slightly from country to country, depending on how each state implements the directive.
8. Ensuring Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
This means:
- knowing where your data backups are stored, how recent they are, who to contact, and who is authorized to perform the recovery
- having a documented Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)
- being able to restore operations after a disruption, outage, or cyberattack
9. Implementing Information Security Policies
This means:
- having basic security policies in place, such as a Security Policy, password policy, access management policy, and other essential guidelines
- maintaining documentation that demonstrates compliance with NIS2 requirements
- keeping clear policies, procedures, and guidelines for employees on how to handle information securely and follow internal security rules
10. Ensuring Ongoing Operation and Continuous Improvement
This means:
- regularly reassessing your situation — including risks, threats, and the effectiveness of existing measures
- performing routine maintenance of your IT equipment and systems
- conducting regular testing and audits to verify the actual security posture
- making updates and improvements to processes, IT equipment, or policies based on audit findings
- managing corrective actions and follow-up measures based on identified issues
- planning regular testing, updates, and maintenance activities