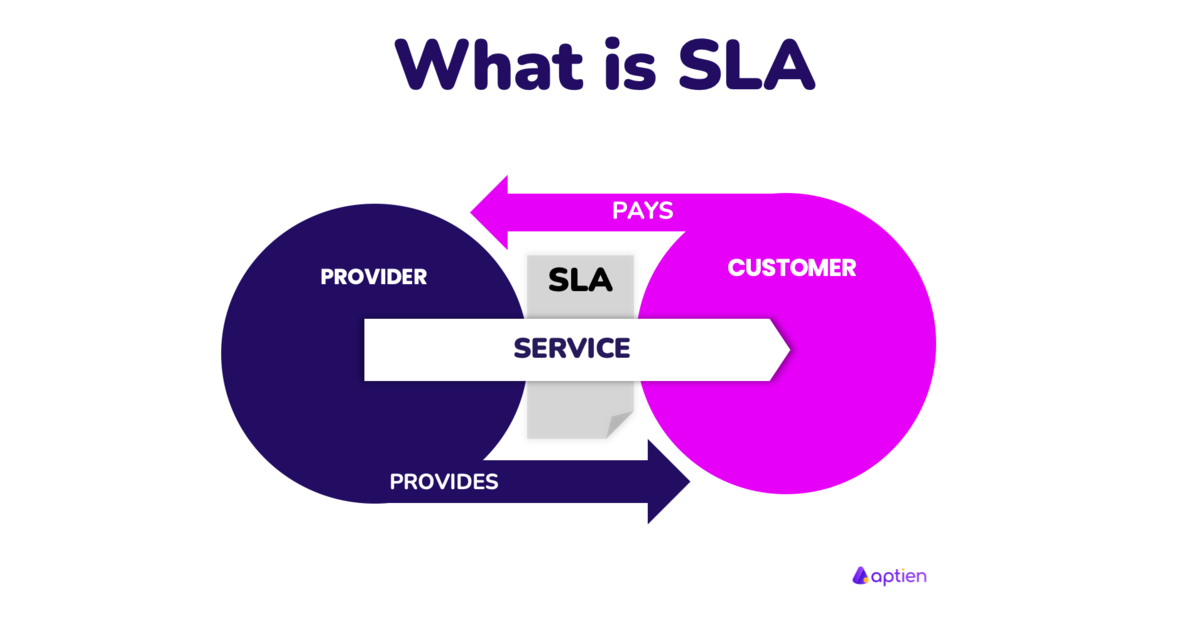
SLA (Service-Level Agreement) is a formal contract or agreement between a service provider and a customer that defines the level of service the customer expects from the service provider. It can be a legally binding contract or an internal company agreement. An SLA outlines specific performance standards, responsibilities, and obligations for both parties, along with consequences if the agreed service levels are not met. SLA terms are used to measure the quality and level of service provided.
What SLAs typically include
- Service scope: Details of the services to be delivered.
- Performance metrics: Clear standards (e.g., uptime percentage, response times) the service should meet.
- Monitoring and reporting: How service performance will be tracked and reported.
- Responsibilities: Roles and duties of both the provider and the customer.
- Penalties and remedies: Actions taken if service levels aren’t met, such as service credits or penalties.
- Review and updates: Guidelines for regularly reviewing and updating the SLA.
What types of services are managed by SLAs
- Commonly used for ongoing or recurring services (for example, internet connectivity)
- Usually not used for one-time services (for example, legal advice)
- SLAs can be part of contracts with external vendors or internal company agreement
What should SLA contains?
Whether the SLA is part of a contract with an external supplier or an internal company agreement, the content of the SLA is usually similar
- Who is the provider and who is the customer of the service
- Customer service expectations
- Key parameters, metrics (KPIs) and limitations of the service
- Tools and ways to measure metrics, quality or performance
- Rewards and penalties for not meeting the required level
- Contacts and escalation processes
What are the most common SLA metrics?
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) use various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to define and measure the quality of service. These metrics can vary depending on the type of service provided. Here are some common SLA metrics you’ll often see:
- Service Availability
- Downtime or Outages
- Uptime Percentage
- Response Time
- Resolution Time
- Capacity (Throughput, Volume, etc.)
- Quality Standards
- Security Measures
- Error Rate
Summary of what SLA is
- The SLA is a agreement which defines the level of service that the service provider gives to the customer
- The SLA is part of the vendor agreement
- The SLA contains metrics and parameters for measuring the level (quality of service) along with penalties for non-compliance
- It is part of the contract for the provision of services between the provider and the customer
- But the SLA can also be introduced internally within the organization, as a definition of the services provided by its other departments