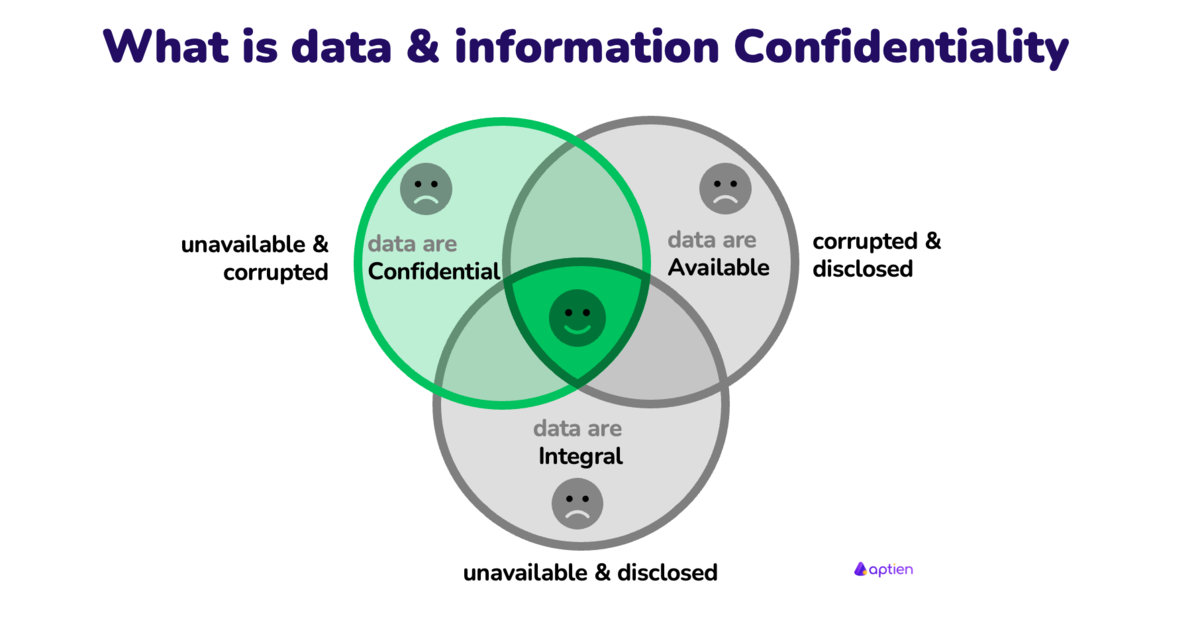
Confidentiality is one of the three quality attributes of data according to the CIA triad of information security and means that only authorized persons have access to the information. Maintaining confidentiality consists in the fact that information should be accessible only to those who are authorized to read it, and therefore it is necessary to prevent access to unauthorized persons. Confidentiality refers to protecting information from unauthorized access.
- Assured confidentiality protects information from unauthorized access and ensuring privacy
- Assured confidentiality prevents misuse of data or information
- Breached confidentiality means that someone unauthorized has access to her data
- Breached confidentiality may lead to misuse of data or information
It is not enough to ensure the confidentiality of data, it must also be available and integral (not corrupted).
How to Ensure Confidentiality in Small and Medium Businesses?
To protect confidentiality, prevent any unauthorized access, changes, or disclosure of systems and information.
How to ensure data confidentiality technically?
- Manage user access with role-based access control (RBAC): grant and revoke permissions during onboarding and offboarding
- Ensure physical security and control employee access to offices, server rooms, and company devices
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit
- Back up data regularly, use the 3-2-1 rule, and test restores
- Secure communications and data in transit (e.g., TLS for web/email, VPN for remote access)
How to ensure confidentiality through processes?
- Screen and vet new hires during onboarding (background checks, verification)
- Remove access and permissions promptly during offboarding (accounts, badges, devices)
Legal safeguards for confidentiality
- Use NDAs (non-disclosure agreements) and add confidentiality and non-solicitation clauses to employment and vendor contracts