Definition of Data Storage
Data storage refers to the systems or media used to store, manage, and protect an organization's valuable data and information. In broader understand data as information assets that include anything from customer data and financial records to intellectual property and operational data. Proper storage ensures that information is secure, accessible, and usable when needed.
Types of Information Asset Storage
Digital Storages
- Databases: Structured collections of data stored electronically, often used for managing large volumes of information.
- Cloud Storage: Online storage services that allow data to be stored and accessed over the internet, providing scalability and remote access.
- Servers: Physical or virtual machines that store and manage data, often used for hosting applications and services.
- Digital Documents: Files such as PDFs, Word documents, and spreadsheets stored on computers or cloud services.
Physical Storages
- Printed Documents: Hard copies of important information stored in filing cabinets or archives.
- Physical Media: CDs, USB drives, and external hard drives used to store data.
People
- People: While individuals themselves are not considered information assets, the knowledge and expertise they possess can be.
- Employees play a crucial role in managing, protecting, and utilizing information assets.
- People use their knowledge and experience to interpret and understand information
AI Systems
- Similar to people AI can be considered an information asset if it generates valuable data insights, or decisions.
- AI systems can also help manage and analyze other information assets.
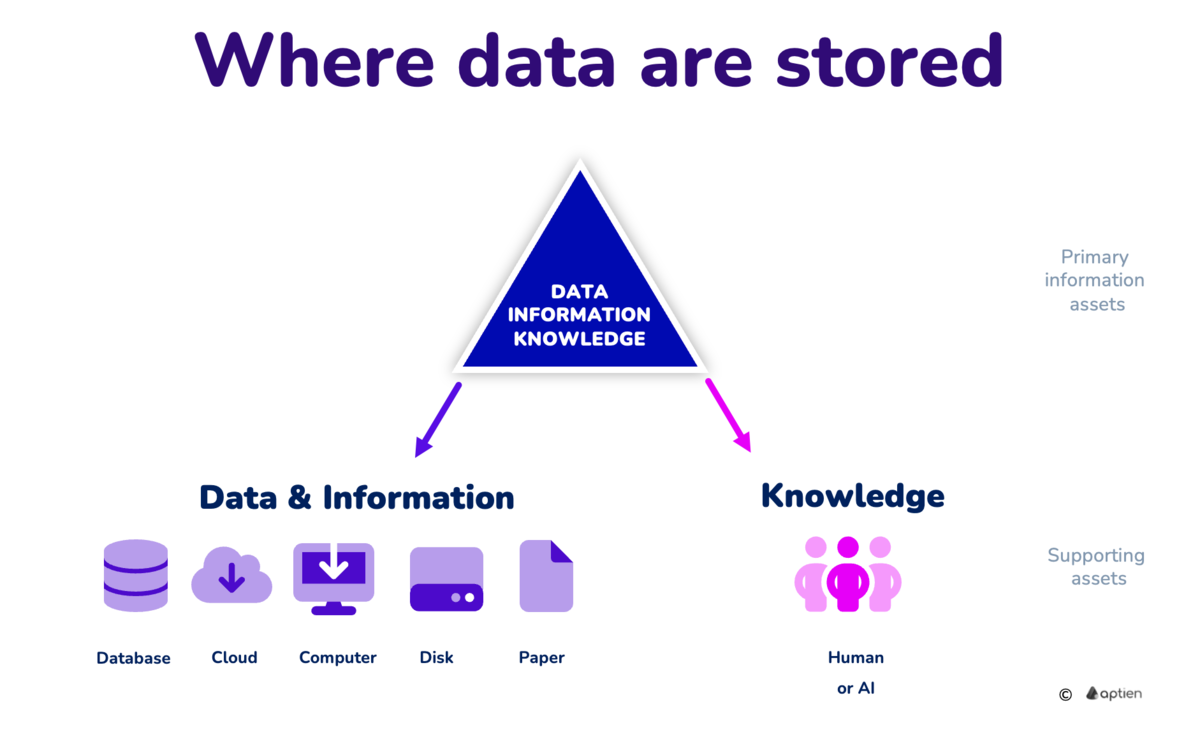
Where are data stored
Any data, information and knowledge must be stored or preserved somewhere. They don't just hang in the air. They exist either in some digital form, on paper, or in someone's head.
The place where they are stored is important from the point of view of information protection and security. Organizations need to know not only what information they need to protect, but also where and how their information is stored to protect the storage itself.
- Data is stored in some application, software, but it can also be stored only on a specific disk, for example, documents can only be stored on one computer
- Printed information is stored on a specific piece of paper, which is physically lying somewhere (and you must know where)
- Knowledge is always associated with a specific person, for example an employee, external worker, business partner or supplier
From a data security perspective, media are supporting information assets.
Why is the data storage important for information security?
The location where data is stored is important for information security management. This is because the individual repositories are:
- the subject of protection or
- subject and part of liquidation processes
The liquidation process ensures that the data stored on the disposed media cannot reach an unauthorized person. The liquidation process is therefore essential when decommissioning hardware, for example decommissioning disks, computers or mobiles on which data is stored. It's the same with shredding paper documents.
Where can data and information be stored?
For the needs of information security, we distinguish the following media and storage most common in practice
Digital media and storages
- database
- hard drive in a computer or mobile phone
- portable disk (flash drive, hard disk, memory cards, USB drives)
- CD, DVD, blu-ray
- Tape drive (typically with data backup)
Physical, non-electronic media
- paper, book
- file binders
- photo
- film
Humans
- employees
- external workers
- suppliers
- business partners, for example a distributor
- customers
How to ensure storage and media security
- for humans it can only be ensured legally, contractually, for example in the form of an NDA
- in the form of digital processes (secure deletion or physical disposal of the media)
- for papers in the form of a physical liquidation process (shredding)
The most important data protection processes from security point of view
Here are the processes that the company must have under control, as they are a frequent source of risks and leakage of sensitive information
- Sale of discarded computers, mobile phones
- Disposal of hard drives
- Employee offboarding