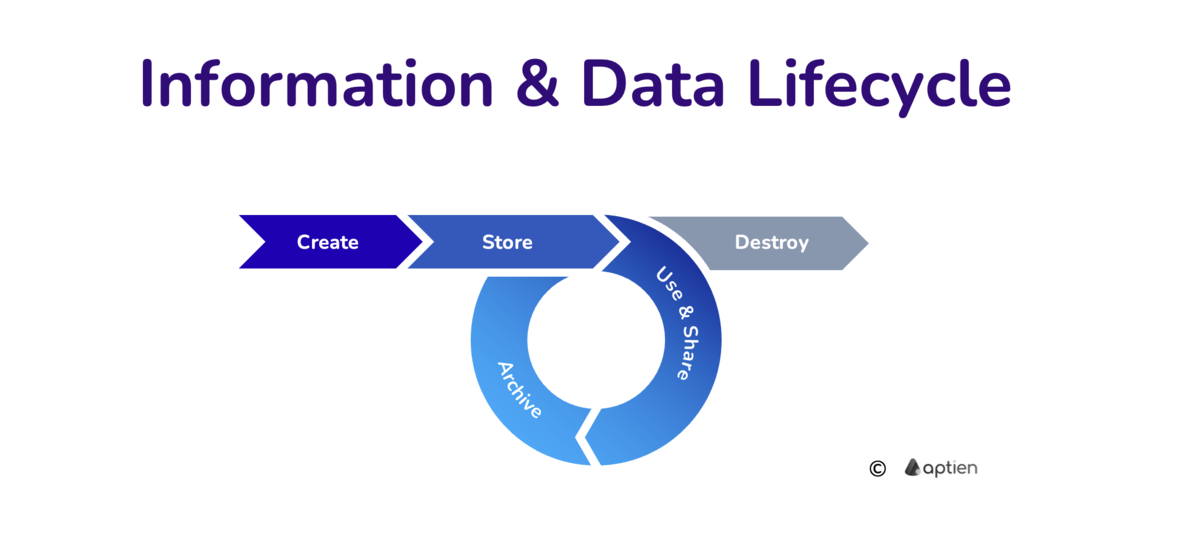
Definition of Information Lifecycle
The information lifecycle includes all phases and processes of managing and operating with information and data. This means from their acquisition, use, sharing to their disposal, archiving or permanent deletion. Information and data are always associated with their carrier and so if we talk about data destruction, it can also mean the destruction of the carrier (for example, shredding of information printed on paper).
- Creation and acquisition of information
- Storing information
- Using and sharing
- Archiving
- Permanent deletion, Destruction and deletion
Creation and acquisition of information
Data and information are created by people by manual input, or they arise in systems, applications, sensors by some measurement, generation, scanning, automatic recording, and so on. Individual systems and applications can be interconnected and so data arises between them by exchange, integration.
- manual input and natural creation of data by people, users
- natural creation by systems, applications, sensors, and so on
- generation
- integration, imports, and data exchange between systems and applications, receiving data from an external source
Storing Information
It is important to emphasize how closely the lifecycle is linked to the carrier, i.e., where and how data, information, or knowledge are stored. Data are acquired and recorded in some form into some system and on some specific medium. Digital or paper form can be destroyed, knowledge protection can only be contractually ensured, because it is difficult to destroy a person as their carrier in regular business practice.
- digital (stored in an information system, software) or
- printed in paper form on paper or
- exist in someone's mind
Using and Sharing
Using data and information is why we have them. Data without use are useless. During their use, they are among other things the subject of protection and information security. Data and information are in the course. It is important to emphasize how closely the life cycle is linked to the carrier, i.e., where and how data, information, or knowledge are. Data are acquired and recorded in some form into some system and on some specific medium. Digital or paper form can be destroyed, knowledge protection can only be ensured contractually, because it is difficult to destroy a person as their carrier in regular business practice.
- protection of access to data
- protection of shared data
Archiving Information
Many data and information have a limited lifespan over time and after its expiration they become unnecessary in normal operation. This does not mean that they cease to exist, but they are subject to archiving (for example, because we need them to prove some fact).
- data retention
- data protection
- archiving
Destruction and Deletion of Information
Destruction, permanent deletion is an important part of data protection. Archived, but also live data sometimes need to be destroyed so that users can no longer use them. Permanent deletion or destruction of data is important in some situations in terms of maintaining data confidentiality. The most common situation in practice is the sale of a company computer, where it is necessary to ensure that the data recorded on it cannot be misused by the new owner. In other words, the data or disk with them "does not fall into the hands of enemies".
In paper form, where information is linked to one medium, paper, it is simpler, shredding paper leads to the permanent destruction of the information stored on it. In the case of digital form of data, it is a bit more complicated, because data can exist multiple times. For example, on a backup disk. Therefore, if there is to be a real permanent deletion of data, it must concern all places and media where this data is stored. In some cases, destruction is associated with the physical destruction of the medium itself, which is the same as in the case of the already mentioned paper. For example, it can be the destruction of a portable disk, so that the data stored on it cannot be misused.
- In the case of information on papers, it is shredding, paper
- In the case of data stored in digital form, it is either permanent deletion
- In the case of selling company devices (computers, mobiles, disks), it is a complete deletion or even destruction of the medium with data
How Aptien will help manage the information lifecycle
- For the needs of information security management, use the primary assets organizer