Definition of Integrity
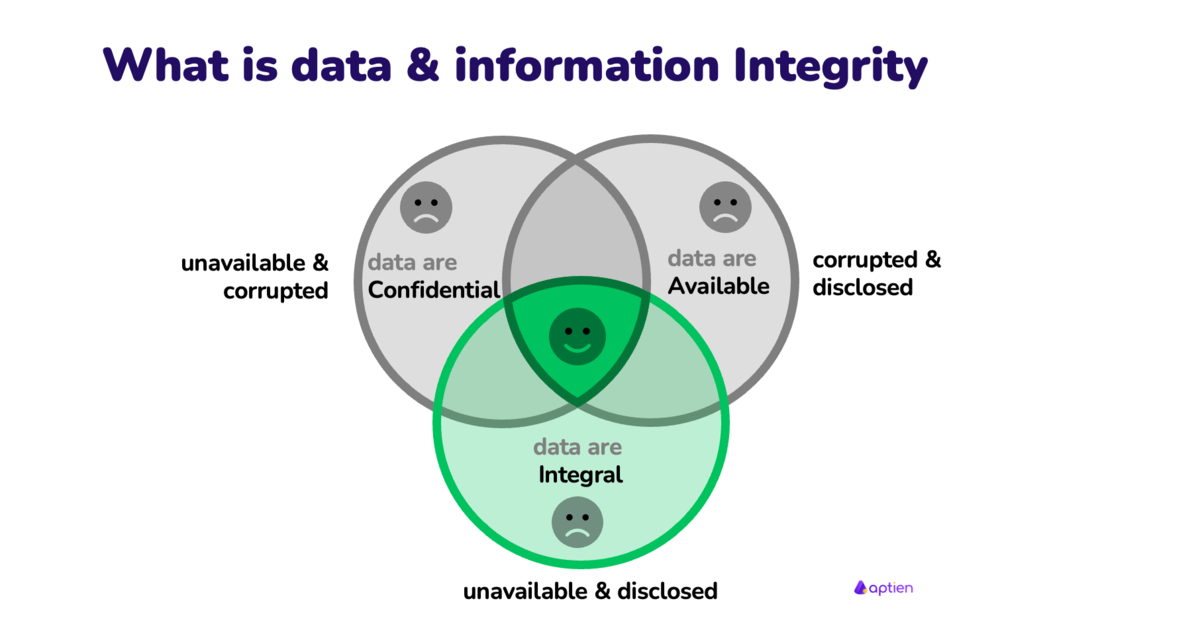
Integrity is one of the three quality attributes of data according to the CIA triad of information security and means that the information is delivered to the user without unwanted changes or modifications. Assured integrity means ensuring the correctness and completeness of information in information systems. The unwanted state is corrupted or altered data.
- Integrity means data are trustworthy, complete, and have not been accidentally altered or modified by an unauthorized user.
- Assured integrity protects data and information from unwanted change
- Assured integrity prevents unwanted change or breach of information
- Disrupted integrity means that the k data is altered and untrustworthy
- Disrupted integrity can lead to loss of trustworthiness or usability of the data
- Partial information is often worse than no information
- Wrong information may lead to disaster
It is not enough to ensure the integrity of data data and information. It must also be available and confidential.
How to ensure data and information integrity in small and medium-sized businesses?
To maintain integrity, it is essential to prevent any unauthorized modification of systems and information.
- Data transmission protection and secure communications (encrypted in transit)
- Data backup
- Data recovery (disaster recovery)
- Protection against eavesdropping and interception
- Background checks for new hires during onboarding