What does availability mean in practice?
Availability means that information, systems, applications, services, and business processes are ready and working when the company needs them. Simply put: what should run, must run. Unavailability (outage, downtime, maintenance window gone wrong, or failure) is a problem because it slows work, causes delays, and can lead to financial losses.
- When availability fails, business stalls — if email, ERP, production, or the supply chain is down, the company loses time, money, and customer trust.
- It’s a security pillar — availability is a core part of cybersecurity (CIA triad of information security).
- It’s measured and committed — for IT services it’s typically defined in an SLA (e.g., 99.9% uptime). In business continuity (BCM), teams set maximum tolerable downtime (MTD) and recovery objectives (RTO for time, RPO for data).
- It guides priorities — companies identify mission-critical systems and processes that must be protected or restored quickly.
In practice for SMBs:
- Availability means keeping the business running with minimal downtime and restoring service quickly when issues occur.
What does availability mean in IT and SLAs (Service Level Agreements)
Availability is the percentage of time a cloud service, application, internet connection, or other IT service is up and running (usable) during a defined period.
- Meaning: a measurable uptime target in a Service Level Agreement (SLA) between a provider and a customer.
- How it’s measured: “nines” of availability (99%, 99.9%, 99.99%) — each level sets the maximum allowed downtime.
- 99.0% ≈ 7 h 12 min of downtime per 30-day month
- 99.5% ≈ 3 h 36 min of downtime per 30-day month
- 99.9% ≈ 43 min of downtime per 30-day month
- 99.95% ≈ 21 min 36 s of downtime per 30-day month
- 99.99% ≈ 4 min 19 s of downtime per 30-day month
In practice for small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs):
- Common for cloud services (email, CRM, ERP) and internet access, where the vendor commits to an uptime SLA and credits or remedies if targets aren’t met.
What does availability mean in Business Continuity Management (BCM)?
It is the organization’s ability to maintain or restore critical activities and assets within an acceptable time after a disruption. In BCM, instead of uptime percentages (SLA), the following terms are commonly used:
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective) – how quickly a process/service must be restored.
- MTD (Maximum Tolerable Downtime) – the longest outage the business can tolerate.
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective) – the maximum acceptable data loss.
- MTPD/MAO (Maximum Tolerable Period of Disruption/Maximum Acceptable Outage) – the maximum interruption before impacts become unacceptable.
In SMB practice:
- Availability applies not only to IT but also to processes, people, facilities, power, and vendors. The company defines criticality and the minimum operating level it needs to sustain.
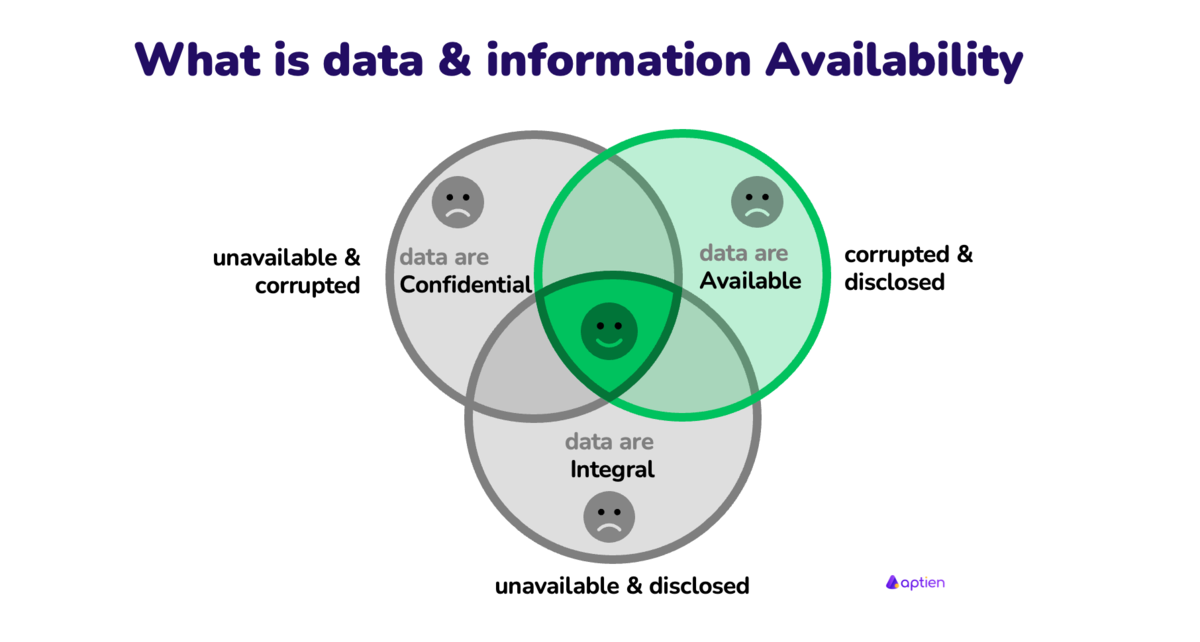
Definition of Availability
Availability is one of the three data quality attributes of data according to the CIA triad of information security and means that the authorized user can obtain data from the system at any time when needed. Assured availability means that the data or information is available, i.e. that it has not been made unavailable. Unwanted state is data unavailability.
- Assured availability protects information from loss or unavailability
- Assured availability prevents loss of data and information
- Broken availability means that the data is not available
- Broken availability can lead to partial or complete loss of data and information
Unavailability can be permanent (for example, when a data carrier is lost or stolen) or temporary (for example, when a system, electricity, or service fails).
It is not enough to ensure only the availability of data and information, it must also be confidential and integral, not corrupted.
What are the basic measures to ensure data availability in a company?
To maintain availability, you need to prevent disruptions to services, systems, or applications, and ensure rapid recovery when incidents occur.
- Data backup
- Data recovery (Disaster recovery)
- High availability for critical systems
- Protection against data theft and encryption-based extortion (e.g., ransomware)