Understanding Risk in Simple Terms
- Risks are potential problems that may or may not occur.
What Risks Mean for Businesses
- Risks are potential problems or challenges you want to avoid.
- They are potential negative events that could harm your business.
- Every risk has a certain chance of happening.
- Risk also represents uncertainty that could prevent you from reaching your business goals.
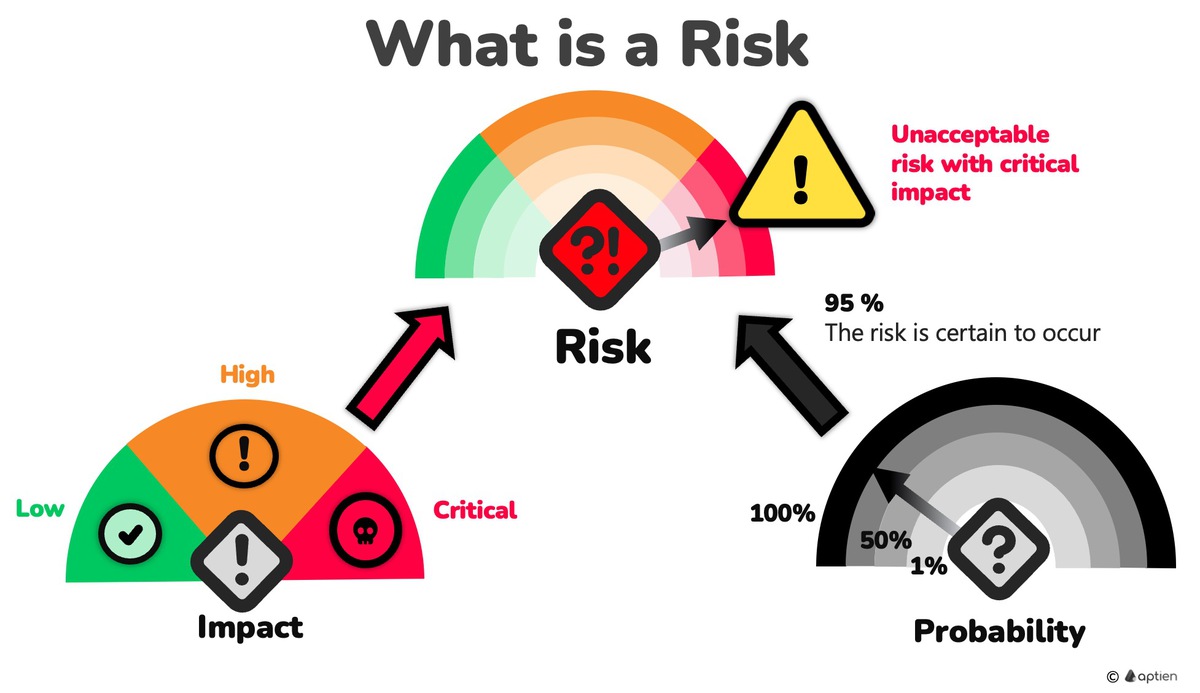
Essentially, a risk is a potential negative event that could affect your business operations, with a certain chance of occurring. When a risk happens, it leads to undesirable impacts and negative consequences for your business.
- Risk = Impact x Probability
The Impact and Severity of the Risk to the Organization
The impact and severity of risks to the organization vary in weight and significance. Each risk's seriousness must be assessed to determine which risks should be prioritized.
- Assessing the extent to which a risk will affect the organization's processes and the seriousness of its consequences is crucial.
- The severity of a risk's impact is derived from consequences and is evaluated through risk analysis.
Example: The impact of an internet outage is critical for an e-commerce solution provider, but only mild for a lawn care company
Likelihood of a Risk
Every risk has a certain probability of occurring. This likelihood is influenced by various factors, some within your control and others not.
- Every process or asset has some level of vulnerability, and higher vulnerability directly increases the likelihood.
- Existing threats also increase the likelihood of the risk.
- Businesses actively work to reduce the vulnerabilities of their assets and processes to decrease the likelihood that a risk will occur.
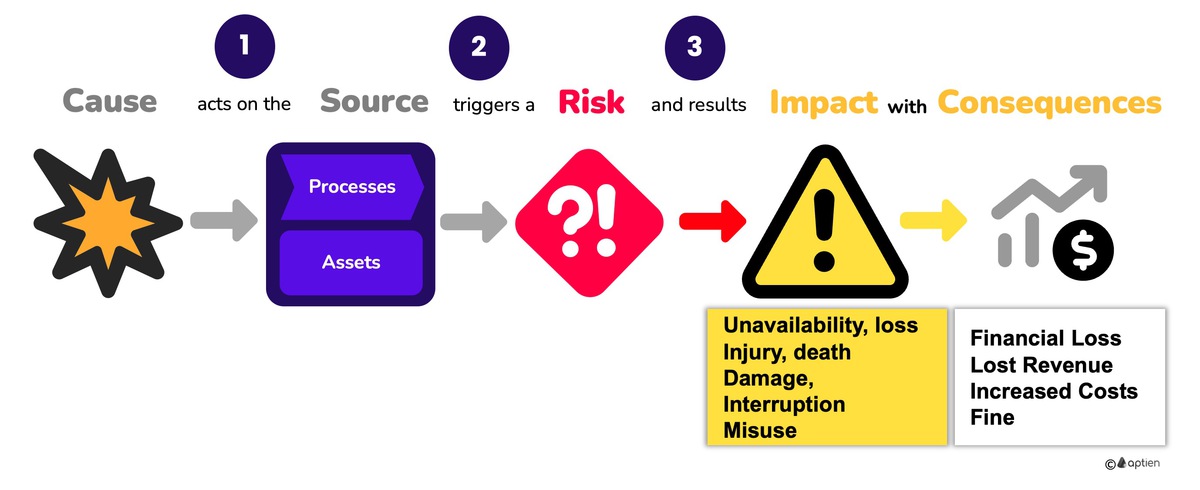
Negative Impacts of the Risk
Once a risk occurs, it creates a problem for your business's operations or assets:
- Disruption or loss of a process, company resources, or other assets, leading to a halt in operations (production stoppage, employee injury or fatality, power outage, data loss, equipment damage, property destruction, theft of funds, etc.)
- Damage takes the form of personal injury, health issues, environmental harm, accidents, data breaches, equipment damage, property damage, and similar issues, resulting in limitations to your processes or asset functionality.
- Misuse involves, for example, unauthorized use or theft of sensitive information (e.g., customer data, trade secrets), and can lead to legal fines, loss of market position, or damaged reputation.
Consequences of the Risk
- These core impacts directly or indirectly lead to financial loss, either through lost revenue (e.g., due to customer churn, reputation damage) or increased costs (e.g., legal fees, operational disruptions, crisis management), or both.
- Ultimately, the overarching consequence of any risk for your business is a financial loss.
How to Write Clear Risk Statements
- It's crucial to define risks clearly so everyone can understand them.
- Learn how to write effective risk statements here.
Common Risks Businesses Face
Every business faces various types of risks across different areas of their operations.
- Financial Risks (e.g., cash flow problems, funding shortages)
- Fraud Risks (e.g., embezzlement, cybercrime)
- Workplace Safety and Health Risks (e.g., injuries, accidents)
- Cybersecurity and Data Protection Risks (e.g., data breaches, ransomware, information loss)
- Reputational Risks (e.g., damage to brand image, negative publicity)
- Competitive and Market Risks (e.g., losing market share, economic downturns)
- Legal and Compliance Risks (e.g., lawsuits, regulatory violations)
- Operational and Project Risks (e.g., business disruptions, process failures, supply chain issues)
- See here for a more detailed description of the most common risks.
Risk Sources
- Risks typically come from your business operations or the assets you use.
- Additionally, risks can stem from various internal and external threats or hazards.
How Aptien Helps Manage Risks for Your Business
Understanding the risks that could threaten your business is crucial for its survival and a key part of effective business management. Aptien provides a clear overview of your risks, including their sources, and helps you keep them under control through planned tasks and actions.
- Learn about the basics of risk management for businesses.
Using a Risk Register
- A risk register helps you identify, evaluate, and track risks.
- It helps manage and assess risks – learn how.