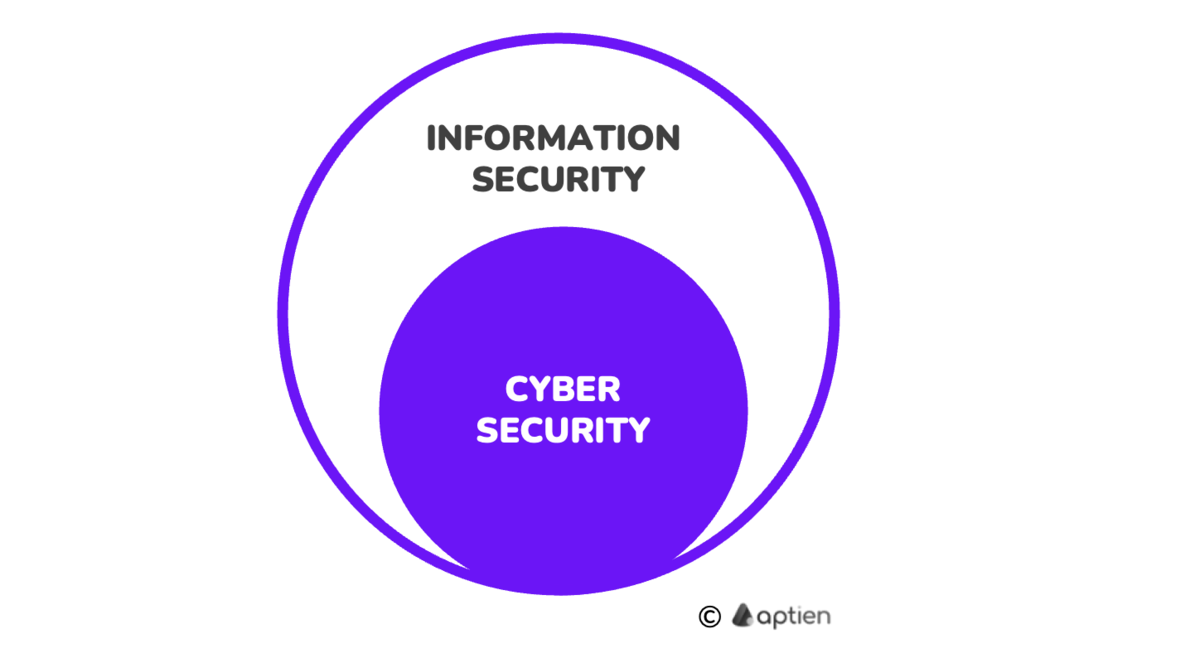
Cybersecurity is a subset of information security that focuses on protecting digital systems and data. Information security, by contrast, covers protecting information in any form, including paper records.
It covers how you protect your data, computers, mobile devices, software, business applications, and networks from hacking, fraud, or data theft. For a small or mid-sized business, this typically includes:
- personal data (customer and employee information)
- money and access to bank or payment accounts
- accounts and login credentials
- photos, documents, and other business files
In short, cybersecurity is about protecting against cyberattacks, such as phishing, malware, ransomware, and account takeover.
What are the biggest cybersecurity threats for companies?
The most common cyberattacks and threats that US small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) should protect against include:
- Identity theft and account takeover (compromised logins, credential stuffing)
- Ransomware and extortion (data encryption and payment demands)
- Malware (viruses, trojans, spyware) and potentially unwanted programs
- Botnets and other command-and-control malware that can take over devices
- Social engineering scams, such as phishing, smishing, vishing, and man-in-the-middle attacks
- DNS spoofing and other methods to hijack or redirect traffic (e.g., domain hijacking)
How to Reduce Cybersecurity Risks in Small and Mid-sized Businesses (SMBs)?
The vast majority of cyberattacks ultimately exploit people’s lack of awareness or weak processes (for example, missing or poor backups). Some types of attacks can be mitigated with technical controls (for example, protection against DDoS attacks or blocking the installation of spyware and malware). Cybersecurity in a company is not only about technology; it must be built on several core pillars:
Staff training and cybersecurity awareness
- Only people educated about potential cyber threats can defend themselves against them
- Cyber education includes recognizing suspicious emails, links or other situations
- Only people following good habits and processes can prevent some cyber risks
Data backup
- Having your data properly backed up is one of the basic precautions
- You can lose data not only as a result of a cyber attack, but also, for example, if you lose your computer
- Data backup is an essential element of data protection
Software and equipment updates and maintenance
- An outdated and unmaintained system, application, software, always poses a greater risk because it potentially contains more bugs and vulnerabilities
- Keep your software up to date
- Use non-obsolete equipment
Strong passwords & behavior
- Use strong, unique passwords
- A good password should be at least 8 characters long and contain upper and lower case letters and numbers
Keep an eye on your devices, computers, mobile phones
- Keep an eye on your devices so you don't lose them or have them accessed by anyone else
- Lock your devices, keep your devices set to log in passwords, PINs or other authentication
- Use good password storage and handling practices
What can happen to your data
Cybersecurity protects your data and information. What are basic data risks? What can happen to it?
- You'll lose your data - for example, if your mobile phone or laptop is lost or is stolen. In short, you lose your data. In the best case, there's no one else to misuse it. For example, you lose all your contracts or photos.
- Someone unauthorised has access to your data. You have your data, but someone else can access it who you definitely don't want to. For example, someone else will know your bank login details. Someone else can get the data - if someone steals your phone and gets in, then you don't have the data and the thief does. He can blackmail you.
- Your data may be altered, either intentionally or unintentionally. You may have the data, but you cannot rely on it or it is altered in such a way that you make bad decisions based on it.