Cyber threats, or cybersecurity threats are any possible malicious attacks on data or an organization's IT equipment that aim to gain unauthorised access to data. Attacks can be random or they can be targeted, organized and may originate from individuals or from a variety of entities, including terrorist groups, hostile national states, criminal organizations, hackers, but can also come from within an organization from disgruntled employees or corporate spies.
What are the most common cybersecurity threats for small and midsize businesses (SMBs)?
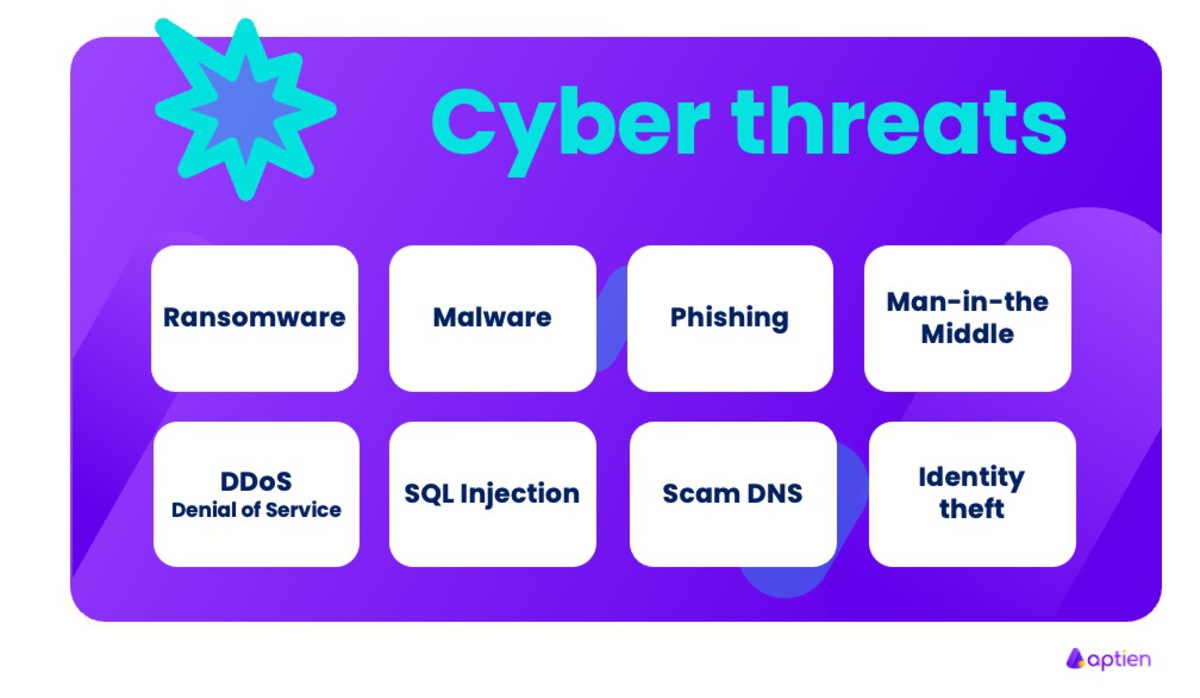
- Ransomware (encrypts your data and demands payment)
- Malware (malicious software like viruses, worms, and trojans)
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks (intercepting communications)
- Phishing – a common social engineering scam
- Identity theft (stolen personal or employee information)
- Data leaks (accidental or unauthorized data exposure)
- Web-based attacks (malicious sites, drive-by downloads)
- Web application attacks (SQL injection, XSS, authentication abuse)
- Botnets (networks of infected devices used for attacks)
- Physical theft, loss, or damage of laptops and mobile devices
- Insider threats (malicious or careless employees/contractors)
- Spam and phishing emails (malicious links or attachments)
- Exploits of software vulnerabilities (unpatched systems)
- Data breaches (unauthorized access to sensitive information)
- Cyber espionage (targeted theft of business or IP)
What Cyber Threats Can Do to the Business
- Cybercriminals can steal sensitive data and use it to break into other systems
- Fraudsters can access bank or payment accounts to steal funds or create costly charges
- Hackers can harvest personal information to scam or impersonate employees or customers
- Attackers can steal intellectual property or trade secrets, hurting your competitive edge
- Data loss or corruption can disrupt operations, damage your reputation, and in severe cases threaten business continuity
Why Understanding Cyber Threats Matters in Business
- Identifying threats (or hazards) is the second step in a risk assessment
- Along with your key assets and vulnerabilities, it helps you pinpoint potential risk
Maintaining an overview of cyber threats is essential for risk management
- Information security risk management requires that you have an understanding of the cyber threats from which the risks arise
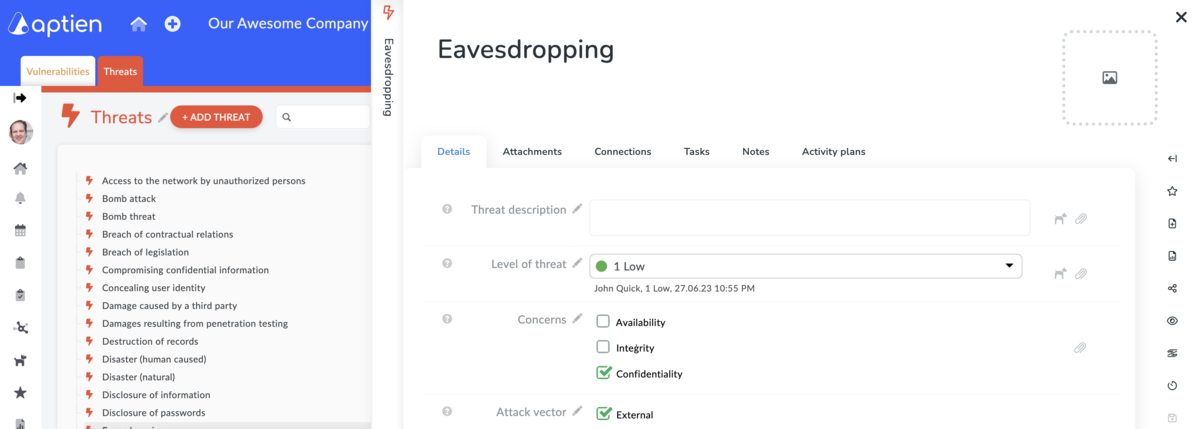
- Creating a list of cyber threats is therefore one of the inputs for risk analysis. Take a look how you can create your computer catalogue Threats