Risk Impact Explained Simply for Business Humans
- A risk's impact is the direct effect or consequence a potential problem has on your business once it actually happens. For example, damaged equipment, service disruptions, computer systems crashing, work delays, lost income, customer dissatisfaction, or employee injuries.
What Risk Impact Means for Your Business
- Impact is the direct result or consequence of a risk event for your business.
- It directly affects your company's operations, processes, resources, reputation, or other valuable assets.
- Common impacts include loss or destruction of property, business disruption, system unavailability, process interruption, injury, data breaches, contamination, physical damage, and more.
- Businesses need to categorize impacts by their severity – often called impact levels (e.g., low, medium, high, and critical).
- It's important to remember: Impact refers to what directly happens as a result of a risk. It doesn't always mean a financial cost, but rather the direct operational or strategic harm caused.
Examples of Risk Impacts to the Business
- Business Operations: Interruptions that stop or slow down your daily work, production, or service delivery.
- Cyberattack: Data loss or damage, data breaches, your computer systems going down, or losing customer trust.
- Supply Chain: Delays in getting what you need, leading to production slowdowns, empty shelves, or losing sales and customers.
- Compliance Violations: Not following laws or regulations, which can lead to fines, operational restrictions, or increased oversight from government agencies.
- Workplace Safety: Injuries to employees, accidents on the job, or tragic fatalities.
Most common risk impacts for SMBs are
- Business Interruptions
- Reputational Damage
- Data Loss
- System Downtime
- Supply Chain Disruptions
- Reduced Productivity
- Equipment Failure
- Data Breaches
- Loss of Customer Trust
- Compliance Violations
- Cybersecurity Incidents
- Employee Injuries
- Product Contamination
- Property Damage
- Decline in Service Quality
Appropriate Words to Describe the Impact of a Risk
- Disruption of
- Damage to
- Loss of
- Unavailability of
- Interruption of
- Reduction in
- Failure of
- Compromise of
- Deterioration of
- Violation of
- Breach of
- Injury to
- Contamination of
- Destruction of
- Degradation of
- Decreased
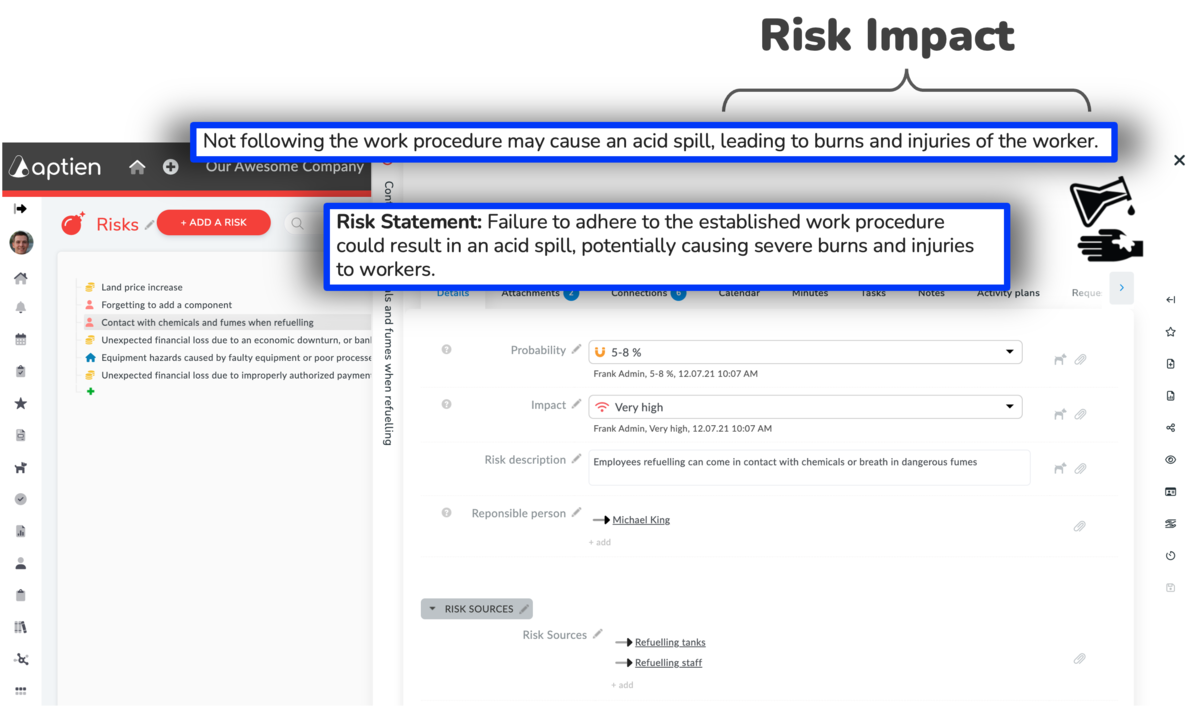
How to Add Risk Impacts to Your Risk Register
- When naming a risk, it's helpful to include its potential impact. This makes it immediately clear what the specific risk could cause.
Steps to Enter Risk Impact:
- Open your risk register.
- Add the risk's potential impact to its name or within its detailed description.
Types of Risk Impacts
- Health and Safety
- Financial Impact
- Data Breach & Privacy Violations
- Legal & Regulatory Penalties
- Criminal Charges
- Reputational Harm & Loss of Customer Trust
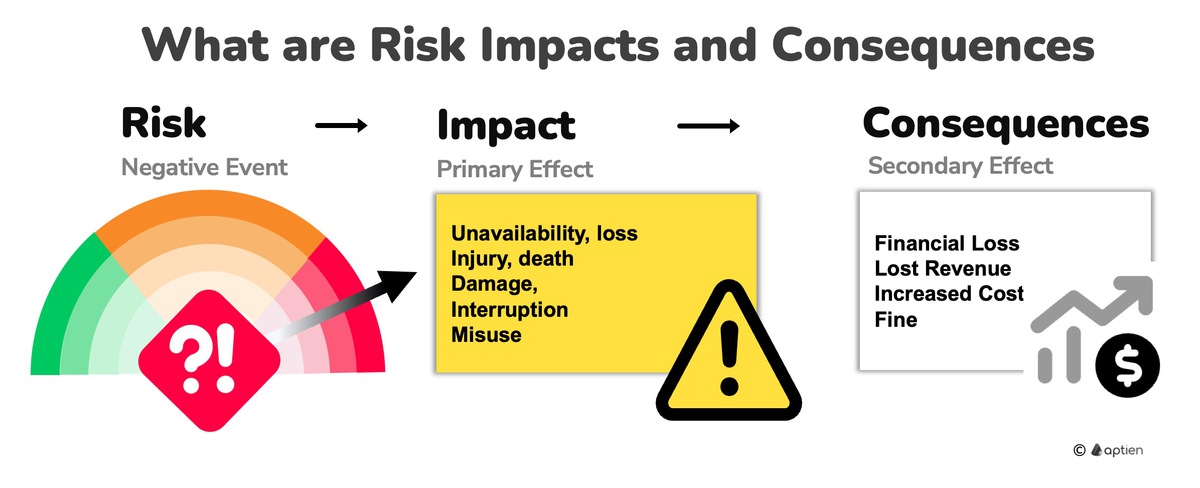
Difference between Impacts and Consequences of Risks
- An Impact is the immediate, direct effect a risk event has on your company's operations, assets, or personnel.
- A Consequence is a secondary, often broader and longer-term outcome that arises from an impact, potentially including financial loss, reputational damage, or loss of customers.
What Are Risk Consequences
- A consequence is what happens after a problem hits your business, directly or indirectly leading to financial loss, either through lost sales (e.g., losing customers, damaging your reputation) or increased costs (e.g., legal bills, business interruptions, emergency management), or both.
- So, the result of a business risk is always a financial cost to your company.
Financial Burden, Financial Loss
- Lower profits because of unexpected bills or lost sales.
- Higher daily operating costs for things like risk management, insurance, or following rules.
- Risk of running out of cash or having trouble paying bills after a financial hit.
Costs of Crisis Management and Recovery
- A lot of time, effort, and money needed to deal with a crisis and get back to normal.
- Stopping or slowing down daily business operations while you handle the crisis.
- You might lose customers and partners while your business is getting back on its feet.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
- Fines, penalties, or lawsuits if you don't follow laws or rules.
- Higher legal bills for defending against claims or settling disagreements.
- Business interruptions because of legal or government investigations.
Insurance Costs
- Higher insurance payments (premiums) or fewer choices for coverage if you've had past claims or are seen as risky.
- Not having enough insurance, which could leave your business exposed to big, unexpected costs.
- Difficulty getting insurance for new or specific risks, leaving holes in your coverage
What Does the Consequence of Risk Mean for Businesses?
- The consequence of a risk is always some form of financial loss for the business.