What Does Risk Management Mean in a Small or Medium-Sized Business?
Risk management in a small or medium-sized business is not just a formality or paperwork for authorities. It is a survival instinct. It’s about making sure nothing catches you off guard and that your company can cope when problems arise. With Aptien, you can handle it simply — using ready-made templates and organizers that save you time and focus attention on what matters: identifying threats, setting priorities, and implementing simple measures. Risk management means that the company:
- knows what can threaten, disable, or even destroy it
- does everything reasonably possible to prevent these situations
- knows what to do if such situations occur and can recover as well as possible
Knowing the risks and being able to avoid them is a basic element of the survival instinct. Risks are obstacles that stand in the way of your goals.
What Risk Management Means for Growing Businesses?
- Risk management helps make sure your business can prevent crises when possible and respond effectively when they happen.
Managing Risks Means Building Business Resilience
Managing risks means spotting potential threats or challenges early. The goal is to strengthen your company’s ability to handle problems and recover quickly with minimal disruption.
What are Key Aspects of Risk Management
- Awareness: Know what processes, people, and assets are most critical to your operations.
- Preventive & Corrective Actions: Put measures in place to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks.
- Response: Make sure employees know roles and steps to take when an incident occurs.
- Recovery: Have plans to restore operations quickly and get back to business as usual.
This practical approach helps small and mid-sized businesses tackle challenges directly and maintain stability during tough times.
What Are Risks?
Risks are possible events or conditions that could harm your business. They might or might not occur, but preparing for them reduces surprises. Risk management means preventing where you can, limiting damage when you can’t, and having a clear plan to respond. Treat risk planning as part of your regular business planning—not just a collection of spreadsheets.
- You can’t predict every risk, no matter how thorough you are.
- Some risks can be controlled or influenced; others are outside your control.
- Risks evolve over time as your business and the environment change.
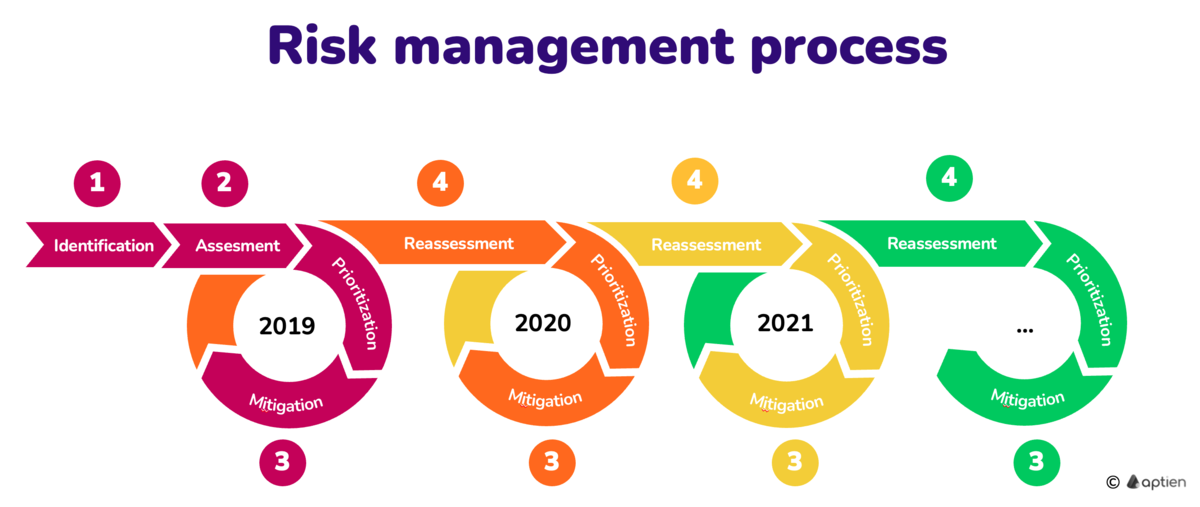
What Is the Risk Management Process?
Risk management is an ongoing process made up of five basic steps:
- Identify the risks
- Assess the risks
- Prioritize the risks
- Address the risks
- Reassess the situation
The process is continuous—just like running a business. Regular monitoring and reassessment help you catch new risks and adjust plans as conditions change. Many small businesses review their risk plan at least annually, or more often when there are major changes.
How to Implement Risk Management in a Company?
Risk management is an ongoing process that starts with identifying potential risks, then analyzing and evaluating them, prioritizing which ones matter most, and deciding how to address each risk. In practice, this is a repeating cycle—similar to annual business planning—that should be reviewed regularly.
To put a risk management program in place for a small or mid-sized US business, you should:
- Maintain a clear inventory of risks and where they come from (operations, finance, compliance, cyber, supply chain, etc.)
- Understand how each risk could impact your people, customers, revenue, and reputation
- Identify the highest-priority risks to your operations and decide whether to mitigate, transfer (e.g., insurance), accept, or avoid them
- Revisit and update your risk assessments and controls on a regular schedule—at least annually or more often when business conditions change
Risk management can be implemented across the entire organization or within specific areas
Small and mid-sized businesses usually start risk management where it matters most to operations and compliance. Common entry points are areas that affect daily operations, customer data, and finances. Before you run a risk assessment, decide the scope—whether you’ll cover the whole company or focus on specific departments or processes. Typical areas to consider include:
- Company-wide enterprise risk management (ERM)
- Workplace health and safety (OSHA / OHS)
- Financial and cash-flow risks
- Information security and data privacy
- Cybersecurity risks
- Other operational or regulatory risks specific to your industry
Risk Register Is a Cornerstone
To support all risk management activities and make improvements over time, you need a central place to store and share risk information. With Aptien you can handle every step of the risk management process, including:
- Build a risk catalog (register/list) where each risk is captured on its own risk card.
- Keep and manage all risks in the catalog, documenting assessments, root causes, impacts, likelihood, and other key details.
- Track sources of risk and the context around them.
- Oversee and assign corrective or mitigation actions.
- Conduct regular risk reviews and re-evaluations.
Step 1: Identify Risks That Could Harm Your Business
Start by listing the risks that could impact your small or midsize business. Use practical approaches like looking at your key assets (data, systems, equipment), mapping critical business processes (sales, payroll, operations), or identifying likely threats (cyberattacks, theft, natural disasters). Put these findings into a simple risk register or catalog so you have a clear inventory to review and prioritize.
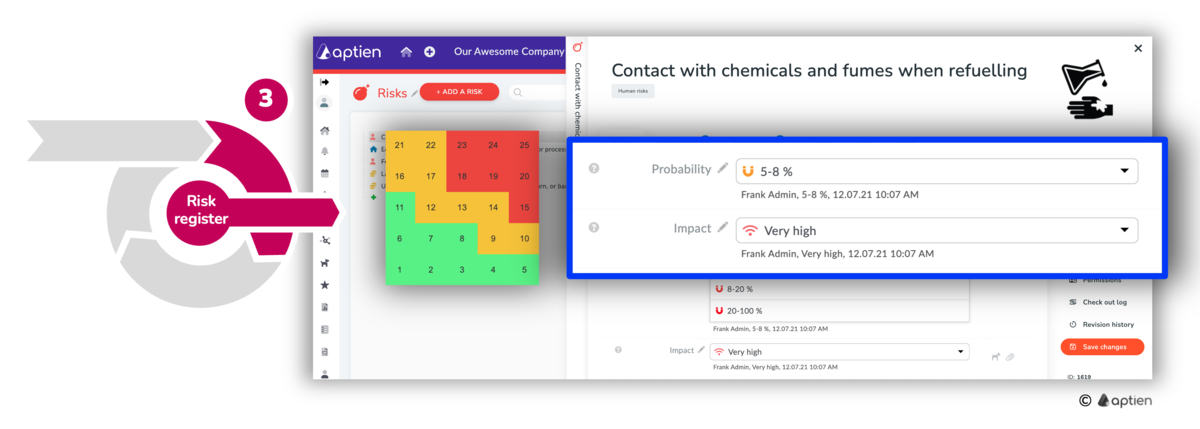
Step 2: Assess and Evaluate Each Risk
After you have your list of risks, review each one on its own. Many teams assess risks as they add them to the list. For every risk, create a simple risk card that records key details like potential impact, likelihood, and recommended actions to reduce or control the risk. Keep these records in a central risk register and include context: link each risk to the related asset—such as a project, location, process, system, or piece of equipment—and assign a clear owner who is responsible for monitoring and managing that risk.
Step 3: Prioritize — Focus on the Risks That Threaten You Most
Using your risk map, prioritize and track risks based on the map’s zones. Click a zone to filter the list and view only the risks that match the criteria you set.
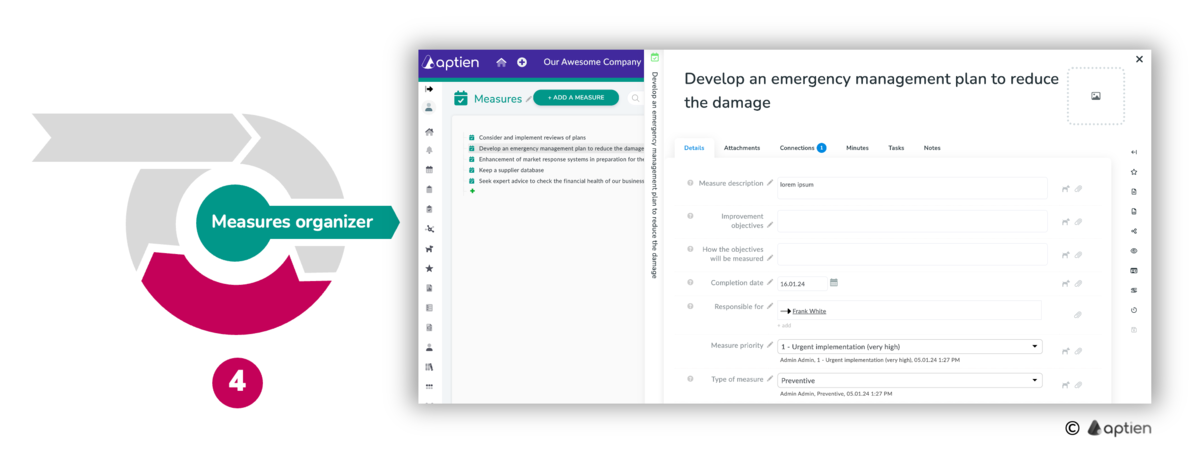
Step 4: Create and Manage Actions
For selected risks, create corrective or preventive actions in a separate action organizer. For each action, create a separate record to store details and use assigned tasks to track and manage the work. Keep risks and their actions linked so you can see which action addresses which risk and who is responsible for each action.
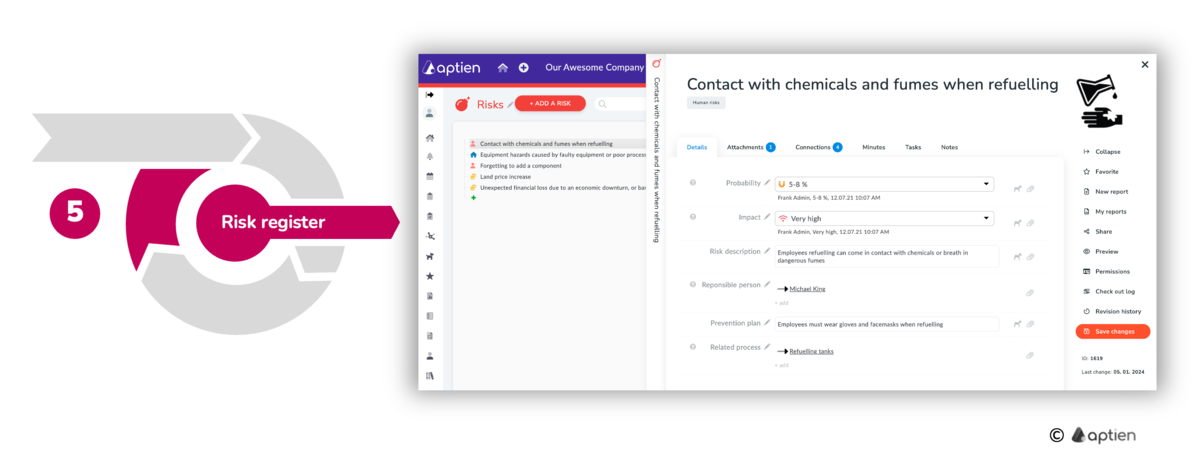
Step 5: Stay Updated and Reassess the Situation
- Risks and business conditions change over time.
- New risks can appear, and existing risks may disappear or change in likelihood and impact.
- At least once a year, revisit your risk assessment and update the actions you take to address those risks.
- Continuously monitor and evaluate your risk landscape. Track the effectiveness of controls, report significant risks, and document mitigation or remediation steps. Use regular reviews and formal audits to identify improvements and trigger re-assessment when needed.