Business Continuity Explained Simply
- Business Continuity is your business's ability to keep operating smoothly, even when unexpected problems or disruptions occur. In simple terms, it means "keeping your business running," no matter what
What Business Continuity Means for Small and Growing Businesses
Business continuity means your company can keep operating smoothly, even when things get tough. For instance, if a key employee is unavailable, a system fails, there's a technical glitch, a fire, or other unforeseen event. The goal is for your business to continue operating without major disruptions or negative impacts on your customers or employees.
Specific Challenges for Small and Growing Businesses
- Small businesses often have only one person in a key role. This means that if that person gets sick or leaves, the business might struggle to keep operating. For SMBs, this often means focusing on:
- Ensuring people are cross-trained – so someone else can step in and take over their work.
Sharing critical information – ensuring it's not just "in one person's head" or buried in their personal files.
How to Address Business Continuity During Outages and Disasters
Business continuity involves two main areas:
- How to prevent operational interruptions – for example, through regular data backups, technology maintenance, or knowledge sharing within the team.
- How to respond when an interruption occurs – which means having a plan of what to do so your business can resume operations as quickly as possible.
Practical Steps for Business Continuity in Your Company
1. Centralize Critical Business Information
- Store all work documents, contacts, and essential information in a centralized company system accessible to multiple authorized team members.
- Avoid storing important files solely in personal emails or on individual computers.
2. Document Work Procedures and Processes
- Document the key steps for all core business activities (e.g., invoicing, ordering supplies, processing customer orders).
- Ensure these instructions are easily accessible so another team member can follow them if needed.
3. Develop a Basic Business Continuity Plan
- It doesn't need to be complex. Simply outline:
- What steps to take during system outages or failures (e.g., who to contact for IT support, where data backups are stored).
- Who will serve as a backup or take over responsibilities for key personnel in case of illness, vacation, or departure.
- Identify the biggest risks to your business and outline strategies to mitigate them.
Threats to Business Continuity
Events that can jeopardize your business processes and operations include:
- Loss of Key Personnel
- Cyberattacks and Data Breaches
- Theft, Vandalism, or Burglary
- Utility Outages (e.g., power, internet, water)
- Technology Service Disruptions (e.g., cloud services, software)
- Supplier or Vendor Failures
- Natural Disasters (e.g., fires, floods, severe storms)
- Other Major Disasters (e.g., explosions, widespread emergencies)
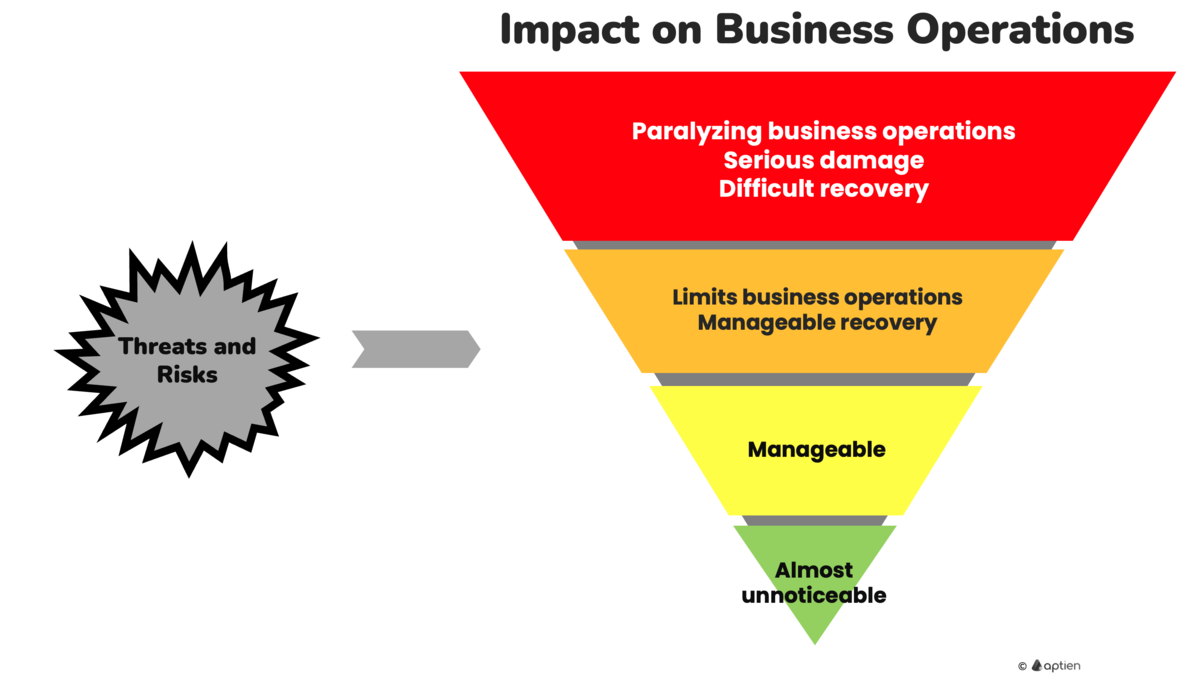
Severity of Impact on Business Operations
- Different disruptions to your business operations have varying effects and levels of severity.
- When assessing and managing business continuity, you should primarily focus on disruptions that would have critical impacts
Business Continuity Management in Larger Companies
In larger companies, managing business continuity is usually part of risk management and IT security. The goal is to ensure that the company can continue to operate even during outages, disasters, or crisis situations. Measures to ensure operational continuity are divided into:
- Preventive measures – help prevent business interruption or minimize its impacts.
- Corrective measures – help quickly restore operations if a disruption occurs.
Preventive Measures for Ensuring Continuity
Preventive measures serve to ensure that the company
- Identifies and understands risks that could threaten its operations.
- Reduces the likelihood of these events occurring.
What do they include?
- Risk Analysis and Assessment: Identify what threats could affect your operations and systems (e.g., cyberattack, fire, long-term power outage).
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Determine which processes and systems are most crucial for the company and whose outage would cause the greatest damage.
- Backup and Redundant Systems: for example, regular data backups
- Preventive Maintenance and Technology Refresh
- Employee Training: Regularly train your team so they know how to proceed correctly in their work and in crisis situations.
- Development of Business Continuity Plans (BCP): Create a plan that describes how to ensure the functioning of key processes during an interruption and how to restore operations as quickly as possible.
- Testing and updating procedures in case of crisis or accident, practicing crisis situations and recovery.
Corrective Measures for Ensuring Continuity
If an outage or crisis already occurs, it's important to be prepared and have a clear plan on how to quickly restore operations.
What do they include?
- Have a prepared and accessible plan, a list of steps on what to do for the most common risk situations.
- Have a backup solution ready and know how to launch or activate it.
- Ensure backup for key personnel, including handover of work procedures.
- Have communication procedures ready for informing employees and customers.
- Arrange for alternative suppliers or services for critical areas.
- Maintain a financial reserve for emergency outages or recovery.
How Aptien Helps Keep Your Business Running
- Identify Business Risks: Pinpoint potential threats and problems that could disrupt your operations.
- Understand Key Operations: Figure out which parts of your business are most crucial to keep running.
- Create Recovery Steps: Develop clear, step-by-step instructions for what to do when disruptions happen.
- Organize Your Rules & Best Practices: Easily share important policies, work instructions, and company best practices with everyone.
- Staff Training: Make sure your team knows what to do by providing training on procedures and workflows.
- Your Business Continuity Plan (BCP): Keep your complete BCP readily available and organized within your guidelines portal.
- Emergency Communication Plan: Set up clear ways to talk to your employees, customers, and partners when things go wrong.
- Regular Review & Updates: Use shared tasks and information to constantly improve your plans and processes.