There are many types of risks that can occur in practice. These risks depend on factors such as the type of business, its size, and the region in which it operates. However, certain types of risks are common across different fields. Here are the main types of risks you may encounter in small and medium-sized businesses:
What are the common types of business risks?
- Employee health and workplace safety risks (People risks)
- Data security and cybersecurity risks
- Competitive, market, and financial risks
- Legal and regulatory compliance risks
- Fraud, theft, and insider risk
- Operational risks — facilities, equipment, and processes
What are the negative consequences of risks?
- Direct financial loss
- Financial responsibility for damages
- Criminal liability for owners or executives
- Regulatory fines and penalties (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, state laws)
- Reputational damage and loss of customer trust
- Lawsuits and legal disputes
Health and workplace safety risks
These risks arise from workplace health and safety violations. People exposed to a hazard may suffer harm or an adverse health effect. Employers are legally responsible for providing safe and healthy working conditions for their employees, and different industries may need to follow a variety of safety requirements.
Examples of health and workplace safety risks:
- Falls, trips and slips
- Hearing damage due to noise
- Electric shock
Ideas for managing health and workplace safety risks:
- Identify and assess hazards, employers and workers
- Regular maintenance of your equipment, workplace and equipment will help prevent workplace injuries
- Good work equipment and trained employees help prevent workplace injuries
- Conduct initial and periodic workplace inspections of the workplace to identify new or recurring hazards.
- Investigate injuries, illnesses, incidents, and close calls/near misses to determine the underlying hazards, their causes, and safety and health program shortcomings.
Security and Cybersecurity Risks
Every company keeps some information, using enterprise applications, employees using mobile devices or computers. Information can be stolen, changed, or hacked. As the use of digital technology grows, cybersecurity risks are growing as well. They are exposed to greater opportunities for hacking, creating security risks for companies and their stakeholders. Both employees and customers expect companies to protect their personal, financial and other business information.
Examples of security and fraud risks
- Data loss
- Loss or paralyzing the information system (application, software)
- Digital identity theft
Ideas for managing cyber-security risks:
- Implement information-cyber-security standards, ISO 27000, NIS2, HIPAA, GDRP, etc.
- Invest in fraud detection tools and software security solutions.
- Educate employees about information and cybersecurity topics
- Use safe applications and enterprise software
- Implement offboarding checklist, (removal of accesses)
Competitive and Market Risks
Every business faces competition, but competitive risk arises when the actions of other businesses negatively impact your company. One of the most significant negative effects of competition is the loss of customers, which can occur for various reasons.
Examples of market and competition risks
- Loss of customers
- Loss of sales
Ideas for managing competitive risks:
- Provide quality products or services
- Provide quality customer service
- Offer a loyalty program
- Ask customers for feedback
Financial Risks
Financial or economic risks impact your profits and, consequently, your company's ability to grow. For instance, if your company's debt exceeds its cash flow, this constitutes a financial risk. Similarly, rising interest rates pose a risk to your cash flow.
Some examples of financial risks include:
- Rising interest rates and financing costs
- Theft or misuse of funds
- Exchange rate risks
- Debt risks
You can implement strategies for financial risks, including:
- Carrying insurance to cover any unexpected accidents or disasters in your business
- Setting aside an emergency fund
- Having an exit strategy for investments your business makes
- keeping debt to a minimum
Legal and Non-Compliance Risks
Legal or non-compliance risks refer to situations that might violate state, local, or federal laws or regulations. To avoid these risks, you need to establish expected behaviors for your employees and suppliers, document them in your policies, and communicate them effectively to your staff. Companies that violate laws and regulatory standards face various penalties and legal risks, including breaches of contracts with suppliers and other partners.
Examples of Compliance and Legal Risks:
- Violation of laws, legislation, regulations, regulatory, or internal standards
- Product liability
- Inconsistency in the operation of devices, machines, and equipment
- Illegal actions of employees
- Failure to comply with legislative safety regulations (OSH)
- Failure to comply with environmental regulations or waste standards
- Failure to follow manufacturer's instructions or recommendations
- Discrimination or harassment in the workplace
Ideas for Managing Compliance and Legal Risks:
- Ensure company policies align with regulatory requirements
- Make sure employees are aware of policies, procedures, and job duties
- Operate the workplace, equipment, and tools in accordance with regulatory requirements
Security and fraud risks
Fraud or security risk relates to any event where persons internal or external to the organization cause harm through deliberate deception.
Examples of security and fraud risks
- Theft
- Loss of material
- Loss of funds
Ideas for managing security and fraud risks:
- Implementation of security measures on both physical (keys, entrance cards, etc) and information assets
- Implementation of anti-fraud processes and systems
Operational Risk
Operational risks include various negative operational events that cause problems in daily processes. Operational risks usually have an immediate, rapid and therefore critical effect.
Some examples of operational risks include:
- Natural disasters
- Theft
- Vandalism
- Failure of technology
Ideas for managing operational risks:
- Most of these events are unpredictable or out of your control,
- Get insurance coverage for your operation
Strategic Risks
Strategic risks arise from your business plan, strategy, and market situation. These risks have a long-term impact and must be identified before they affect your company's finances. Strategic risk management is typically part of strategic management and planning.
Examples of Strategic Risks:
- Changes in the market
- Changes in the geopolitical situation (e.g., war)
- Technological changes
- Legal changes
- Competitive pressure
- Shifts in customer demand
Ideas for Managing Strategic Risks:
- Make informed strategic decisions
- Ensure access to quality information for strategic decisions
Reputational Risk
Reputational risks involve the harm of your business’ public image. This can come from a negative news story creating bad publicity or customers having poor experiences with your business. Either way, brand loyalty is often damaged, which ultimately reduces your profits and your customer base. Reputational risks can arise from compliance, security or fraud risks.
Some examples reputational risks include:
- Defective products
- Negative posts on social networks
- Leakage of sensitive information
Ideas for managing reputational risks:
- Addressing customers that write negative reviews and helping find a solution
- Encourage customers to write positive reviews
- Invest in cybersecurity
Summary of good practice for risk reduction
- Regular education and training of workers and thus educated employees help prevent injuries in the workplace
- Regular maintenance of your equipment and equipment will help prevent workplace injuries
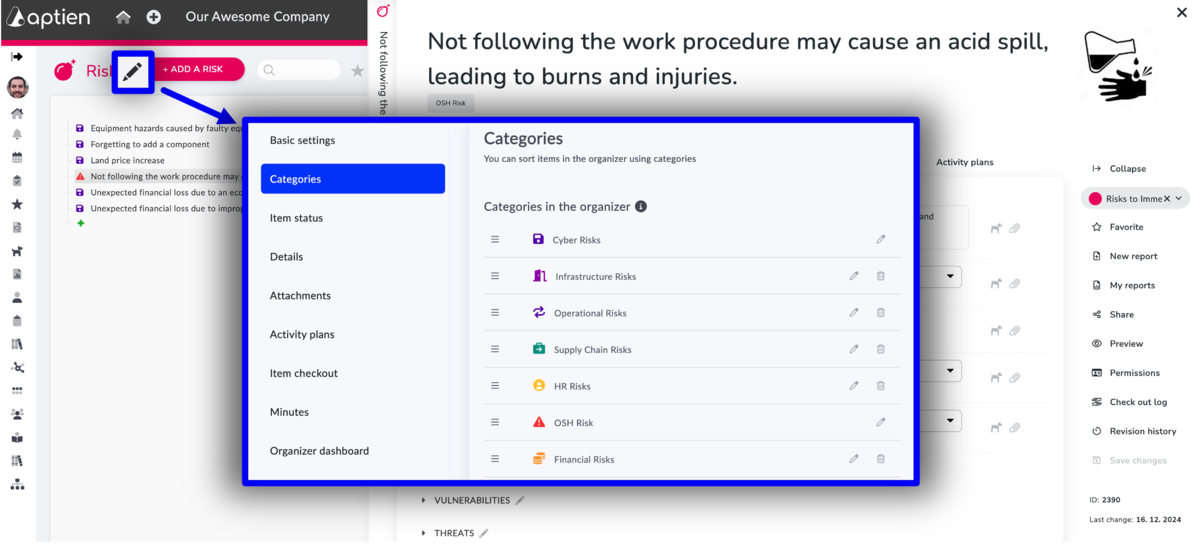
How to change risk types?
You can easily change the default risk types to match your methodology. You use categories for this.
- As an Administrator Go to the Risk register settings
- In Risk Register Settings, select "Category"
- Make changes in the list or rename existing risk types
- If you use multiple languages, be sure to change both the primary and secondary languages
- How to create, edit or delete categories can be found in this article