Explanation for business humans what is Job, Simply
Job is a like a template for describing a specific role within a company, outlining what a person in that position does: including the tasks, main responsibilities, requirements, and duties.
What a Job Means for Growing Companies?
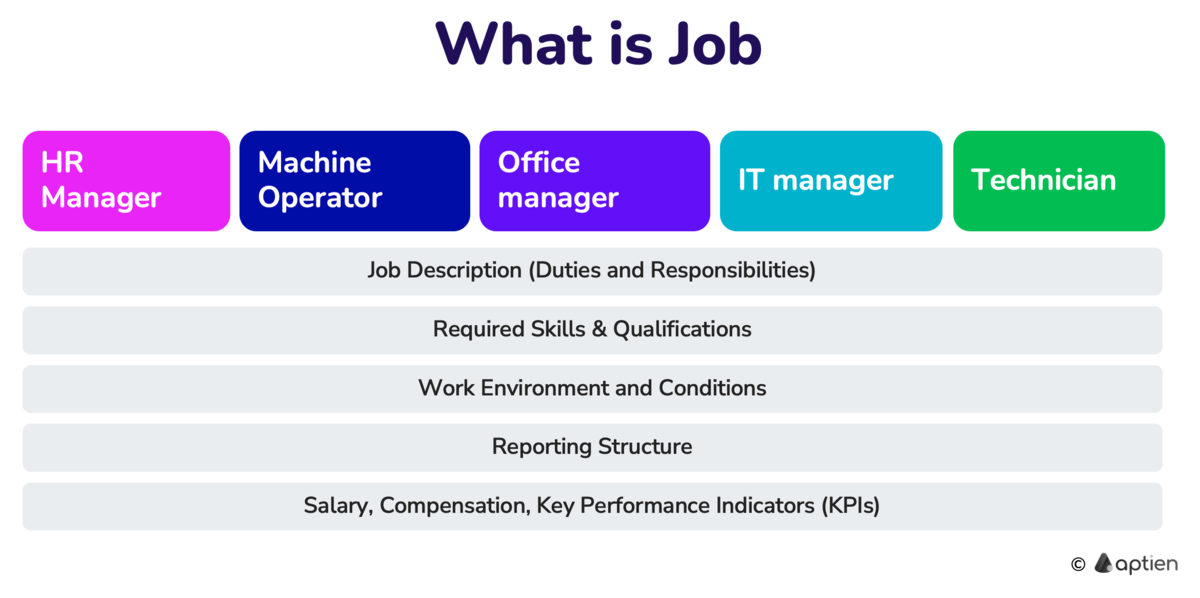
A general category of work that outlines the essential requirements, tasks, responsibilities, and skills needed. Think of it as a broad description of the work. Multiple specific roles can fall under one job. For example, "Marketing Specialist" is a job title, while a specific role within a company's marketing department is a position. You might say, "Her job is Marketing Specialist." A job description typically includes:
- Basic requirements for performing the work.
- An outline of typical tasks.
- Necessary skills and knowledge.
- Required qualifications.
A job position helps keep a consistent description:
- what is done in the position, its main responsibilities, authority, and duties
- what is required from the person doing the job
- what the working conditions are
Companies use the job position for:
- A clear description of the job role (basic requirements for performing the work, main tasks)
- A list of qualification requirements
- A checklist for onboarding a new employee
- A list of necessary work tools
- A list of required training
- A list of needed permissions (keys, cards, access to applications)
How to describe a Job?
- Job Title: The name of the position (e.g., "Marketing Manager") that reflects its function and seniority.
- Job Duties: Specific tasks and activities involved in the job.
- Job Responsibilities: Specific tasks and activities the role involves.
- Job Qualifications: Education, experience, skills, and other prerequisites needed for the role.
- Work environment and conditions: Any working conditions, such as equipment, tools, remote work options, or physical demands.
- Location in the organizational structure: Reporting structure and any supervisory responsibilities.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics used to measure success in the role.
Why do Companies Need Jobs?
- Standardizing work performance: Multiple people perform the same job, and it needs to be described in one place. A job description allows clear and understandable expectations across the company.
- Ensuring continuity: When responsibility is tied to the position, the company keeps running even when people change (e.g., illness, vacation, departure). When an employee leaves, it’s clear what the successor should take over – because the position has its own “content.”
- Better company growth management: Positions are the "building blocks" that enable capacity planning, hiring, and delegation.
- Easier hiring and onboarding: When job roles and descriptions are clear, it’s obvious who you’re looking for and what they will do.
- Employee development and evaluation: Job positions allow planning training and development based on the needs of the role, not the individual. They enable performance evaluation based on job duties, not personal feelings.
Why Defining Responsibilities by Job Title is Better Than by Employee Name
In small businesses and teams, focusing on individual employees instead of standardized job titles is a common mistake. Often, responsibilities and requirements are tailored to specific people. However, as the team grows and multiple people perform similar tasks, standardizing job content becomes crucial. This is where well-defined job titles become essential.
- "Personal" management is effective for teams of up to 5 people.
- Beyond 5 team members, it's common for multiple individuals to share similar responsibilities.
- This creates a need to base job descriptions and people management on standardized job titles.
Company Size Guidelines for Implementing Job Titles:
- 1–5 people: Roles can be assigned more informally, "by name."
- 6–15 people: The ideal time to introduce job titles with clear job descriptions.
- 16+ people: Without defined job titles, you risk chaos, inefficiency, and confusion.
Reasons for Creating Job Titles
- Standardize Work Performance: When multiple people do similar work, a single, clear description is essential. A job title description provides company-wide clarity and consistent expectations.
- Ensure Business Continuity: When responsibilities are linked to a job title, the business functions smoothly, even when employees are out (sick leave, vacation, turnover). When someone leaves, their replacement understands their responsibilities because the position has a defined "scope."
- Manage Company Growth Effectively: Job titles act as "building blocks" for planning capacity, hiring, and delegation.
- Streamline Recruitment and Onboarding: Clearly defined duties and descriptions clarify the type of candidate you seek and their responsibilities.
- Facilitate Employee Development and Performance Reviews: Job titles help you plan training and development based on the needs of the role, not individual preferences. You can then evaluate performance against the job description, not personal biases.
What is the difference between a Job and a Position?
- In common practice in small and medium-sized businesses, these two terms are often used interchangeably.
- Job is a more general term that refers to a set of tasks, responsibilities, and skills needed to perform the work. It's often used as a synonym for "job title" but may emphasize the specific duties of the role. For example: "His job title is Senior Accountant."
- Position refers to a specific role within the company's organizational structure. It exists whether or not someone is currently filling it. It represents a defined place within the company, independent of a specific person. For example: "We have a vacant Accountant position."
How to Name Job Titles Effectively
- Consider job title naming before creating the position
- The title should be clear and easily searchable
- See best practices for naming job titles effectively within your company
How to Describe a Job
- The focus of each section of a job description can change based on whether you're hiring or creating a description for an existing employee.
- When hiring, emphasize the qualifications and experience the ideal candidate should possess.
- For internal work management, highlight the job's responsibilities, its position within the company hierarchy, and the necessary tools or permissions required to perform the job effectively.
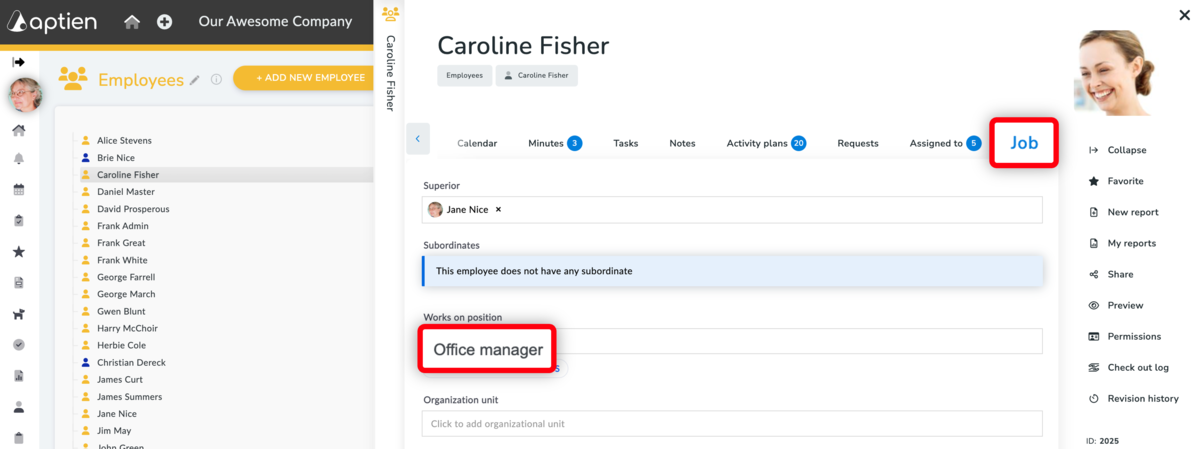
How to Create and Manage Job Positions in Aptien HR
- See how Aptien helps you create and manage job positions within your company
How to Assign an Employee to a Job?
- In small and medium businesses, employees usually have individual job roles
- Managers typically hold individual job roles because their responsibilities are unique
- In larger companies, a single job role may be shared by multiple employees, especially in blue-collar positions where duties are the same
- For HR professionals, shared job descriptions and specifications make the process much easier
- The larger the team and company, the more common shared job roles become