Understanding the Back Office in Business Operations
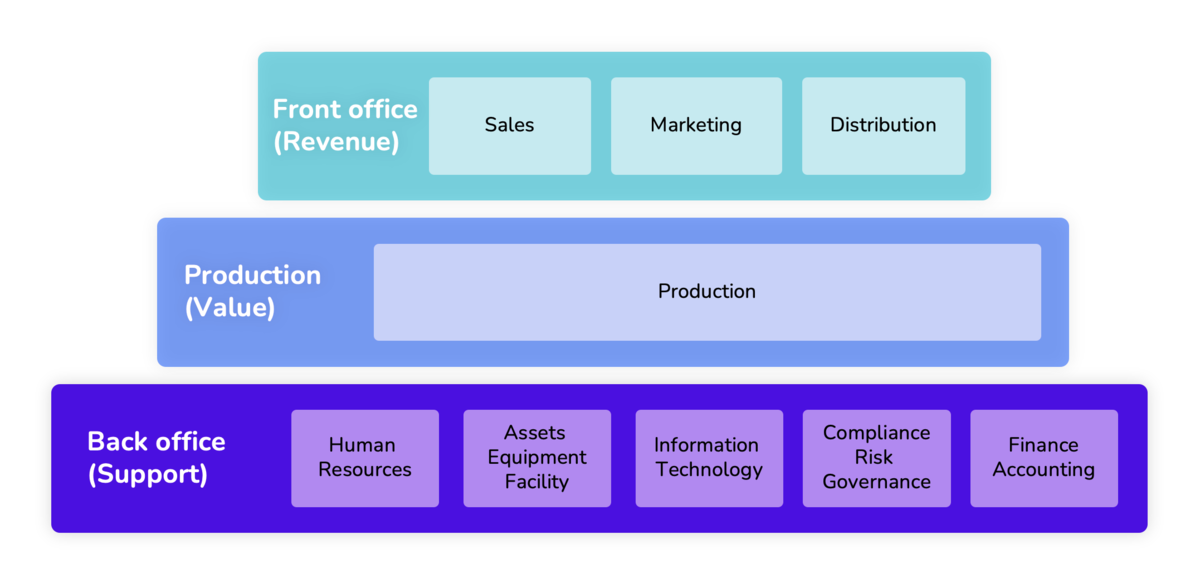
The back office (also called the back-end office) includes the internal business functions and administrative tasks that keep a company running smoothly. Simply put, the back office supports a company’s main operations by managing essential support activities. Its main purpose is to help employees, improve efficiency, and ensure smooth day-to-day business operations.
The back office (back-end office) focuses on internal tasks that keep a business running behind the scenes. In other words, the back office covers the support functions that help the company operate efficiently. Its goal is to support employees and boost overall business performance.
What are key functions of the Back Office?
The back office is the backbone of a company’s internal operations, making sure everything runs smoothly across departments. It typically includes the following functions:
- Human Resources (HR) – Manages employee tasks such as hiring, onboarding, payroll, benefits, compliance, and offboarding.
- Facilities, Asset, and Equipment Management – Maintains company properties, office spaces, equipment, and handles repairs.
- Information Technology (IT) – Oversees data systems, software, cybersecurity, and communication networks.
- Compliance, Risk, and Governance – Makes sure the business follows laws, industry standards, and internal policies while managing risks.
- Finance and Accounting – Handles financial transactions, budgeting, expense tracking, taxes, and financial reporting.
By managing these functions well, the back office plays a key role in keeping operations steady, improving efficiency, and supporting business growth.
Who is Responsible for the Back Office?
The responsibility for managing the back office varies depending on the size and setup of the company. As businesses grow, these duties are often split among different roles to improve efficiency and focus. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Back Office in Small Businesses:
- Responsibility: In small businesses, back-office tasks are usually handled by the owner, CEO, or an administrative assistant. These people take care of administrative work, HR basics, simple accounting, and IT support.
Back Office in Medium-Sized Businesses:
- Responsibility: As the company grows, back-office responsibilities are typically divided among specialized positions:
- Office Manager: Manages daily office operations and helps coordinate between teams.
- Human Resources (HR) Manager: Handles hiring, employee relations, payroll, and benefits.
- IT Manager: Takes care of technology systems, maintenance, and data security.
- Facilities Manager: Looks after the upkeep and functionality of office spaces and equipment.
Back Office in Large Businesses:
- Responsibility: In larger companies, back-office functions are usually overseen by senior leaders:
- Chief Operating Officer (COO): Oversees daily operations, including back-office activities.
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO): Manages financial matters and may oversee HR and IT departments.
- Back Office Manager: Focuses on managing back-office teams and ensuring smooth internal processes.
No matter the company size, a well-managed back office is key to keeping operations running smoothly and supporting business growth.
Examples of Back Office Jobs
Every company's back office looks different and the job can vary depending on the size of the company and the industry. Here are some examples of back-office jobs, with basic information about their primary responsibilities.
- Office manager
- COO Chief operating officer
- HR professional
- IT manager
- Facility manager
- Compliance manager
- Accountant
- Security manager
- Risk manager
- Assistant