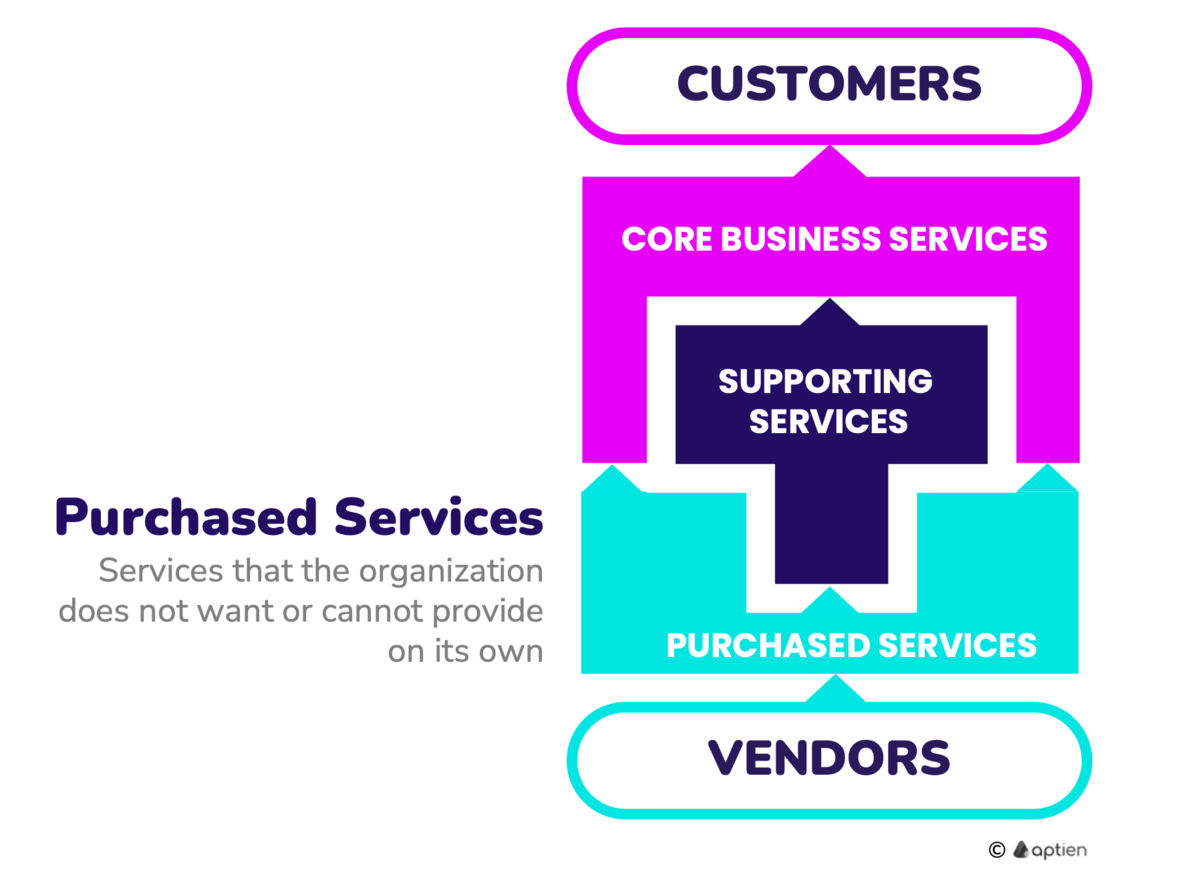
Purchased services are services that a company either cannot provide itself or chooses to hire from outside providers.
Why Purchased Services Are Important for Growing Businesses?
1. Enabling scalability as the business grows
- Purchased services can scale quickly as business needs change, supporting expansion without delays tied to hiring or internal training.
2. Enabling focus on core business
- By purchasing services for non-core functions, managers and employees can focus their time and energy on what directly drives revenue and growth.
3. Access to expertise and capabilities
- Small businesses often lack in-house specialists for areas like IT support, marketing, HR services, cleaning, security, or equipment maintenance. Purchased services give them immediate access to professional expertise without needing to hire full-time staff.
4. Cost efficiency and flexibility
- Outsourcing services can be cheaper than building internal capabilities, especially for tasks that are not core to the business. It allows companies to pay only for what they use and adjust services based on demand.
5. Improved quality and compliance
- Professional service providers often ensure better quality, adherence to standards, and regulatory compliance than an internal ad-hoc approach.
6. Risk reduction
- Relying on experienced providers reduces operational risks, such as equipment downtime due to poor maintenance or compliance failures in HR or safety processes.
What Services Are Small and Growing Businesses Purchasing or Outsourcing?
Businesses often hire outside services because it’s more cost-effective, required by regulations, or they don’t have the expertise in-house. Purchased services are those a company either can’t provide internally or chooses not to. Companies outsource these services for convenience or because they lack the necessary skills or resources. These external providers help support day-to-day operations or deliver key business functions. Outsourcing allows businesses to tap into specialized knowledge, lower costs, and focus on what they do best.
Many services are bought from outside vendors, but an internal team is always responsible for managing and overseeing the purchased service.
Examples of Purchased or Outsourced Services
- Energy supply
- Banking and account management
- Insurance
- Transportation services
- Maintenance of machinery and equipment
- Accounting services
- Payroll processing
- Internet service
- IT support and services
Purchased services are those acquired from third-party providers to help run a business, meet specific needs, or improve capabilities. Outsourcing these services lets small businesses access expert skills, reduce expenses, and concentrate on their core operations.
Why Businesses Purchase Services?
Limited Staff and Resources
- Small and growing businesses often lack sufficient in-house specialists or capacity for all support areas (e.g., IT management, cybersecurity, accounting, HR processes). Therefore, they purchase services from external providers to save time and costs.
Focus on Core Business
- Outsourcing allows them to focus on their core business – for instance, a construction company focuses on building, not on server management or payroll processing.
Scalability and Flexibility
- External services enable them to grow faster and adapt to demand, because they are not buying one-off people or equipment, but rather capacity and expert know-how according to current needs (e.g., number of SaaS licenses, cloud server capacity, scope of legal or accounting support).
Quality and Professionalism
- External service providers often bring higher quality and expertise than if the company were to secure services internally with limited know-how.
Best Practice for Purchased Services and Vendor Management
Managing purchased services effectively requires implementing best practices to ensure cost efficiency, quality, and vendor reliability. Here are some fundamental best practices for managing purchased services:
Develop a Vendor Selection Process
- Research and Shortlist Vendors: Use online reviews, referrals, and vendor marketplaces to identify reliable providers.
- Request Proposals (RFPs): Solicit detailed proposals, including pricing, service delivery, and terms.
- Evaluate Vendors Based on KPIs, SLAs: Assess vendors on cost, quality, experience, and reliability before making a decision.
Ensure Vendor Compliance, Manage Vendor Risks
- Vendor Due Diligence: Verify the vendor's compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Risk Assessments: Regularly evaluate potential risks such as over-dependence on a single vendor or data security issues.
Keep Minimum Contractual Requirements with Vendors
- Detailed Agreements: Include clear terms for deliverables, timelines, costs, penalties for non-performance, and termination clauses.
- Use service level agreements (SLAs) for Performance Metrics: Use KPIs (e.g., delivery time, quality, cost-effectiveness)
Maintain Strong Vendor Relationships
- Transparent Communication: Keep history of communication, to avoid business discontinuity.
- Maintain Records: Store contracts, service level agreements (SLAs), and correspondence in a centralized, easily accessible location.
Monitor Service Quality
- Regular Check-Ins: Establish a communication schedule with vendors to monitor progress and address concerns promptly.
- Performance Metrics: Use KPIs (e.g., delivery time, quality, cost-effectiveness)
Automate Vendor and Service Management
- Use SaaS Tools: Leverage software to automate workflows, track vendor performance, and manage contracts and payments.
- Reminders and Alerts: Automate notifications for contract renewals, payment deadlines, and performance reviews
How Aptien helps you Manage Outsourced Services and its Suppliers
Aptien solutions tailored for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can significantly streamline the management of purchased services and their vendors. Here’s how they can help:
1. Centralized Vendor Management
- Central Company and Vendor Database: Maintain a centralized repository for all vendor information, including contact details, contracts, service agreements, and payment terms.
- Category-wise Organization: Classify vendors by service type (e.g., IT, maintenance, marketing) for better visibility and management.
- Performance Tracking: Rate and evaluate vendor performance based on predefined KPIs.
2. Contract and Service Management
- Contract Repository: Store all contracts digitally with search functionality for quick access.
- Renewal Reminders: Set automated alerts for contract renewals or expiration to avoid service disruptions.
- Terms Compliance: Track compliance with contract terms using audit logs or task management features.
3. Purchase Order and Invoice Management
- Purchase Order Automation: Generate, approve, and track purchase orders (POs) within the platform.
- Invoice Matching: Match invoices to POs and service agreements to ensure accurate payments.
- Expense Tracking: Categorize expenses to monitor spending patterns and identify cost-saving opportunities.
4. Workflow Automation
- Approval Processes: Automate vendor approval workflows to ensure compliance with company policies.
- Task Management: Assign and track tasks related to vendor onboarding, service delivery, or dispute resolution.
- Notifications: Receive alerts for critical activities such as contract milestones or service outages.
5. Collaboration Tools
- Communication Hub: Facilitate communication with vendors through integrated messaging or email.
- Shared Portals: Provide vendors access to a secure portal for document sharing, invoicing, and updates.