Reactive maintenance addresses failures and repairs
Corrective, reactive maintenance is simply handling breakdowns and failures. Reactive maintenance responds to a failure after it occurs — unlike preventive maintenance, which aims to prevent failures.
Examples of corrective maintenance tasks
- repairing equipment after a user reports a problem
- fixing faults found by monitoring systems
- repairing defects found during routine inspections
- resolving incidents that interrupt operations
How to Report Faults, Defects and Failures
- Most reactive maintenance starts when someone reports a problem or equipment failure.
- Make sure you have a simple, reliable reporting system so staff can report a fault. Reports should enter a clear workflow so a responsible person or technician picks them up and fixes the issue promptly.
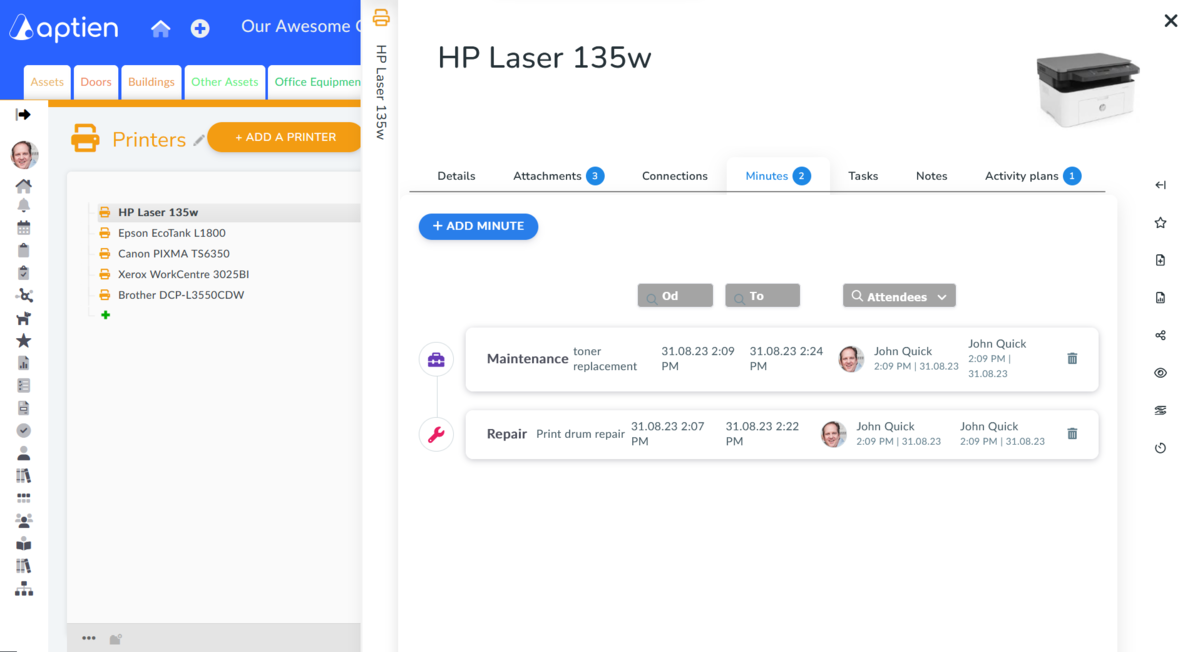
How to Keep Maintenance Records
- After a maintenance worker fixes a fault, record the repair in the maintenance log for that equipment.
- These records help with follow-up, troubleshooting future problems, and keeping a clear history of work done on your equipment.