Definition of Enterprise Information System
An Information System (IS) encompasses people, processes, data, and software and hardware working together to collect, process, store, and distribute information within an organization. Its purpose is to support decision-making, coordinate operations, facilitate communication, and achieve organizational goals efficiently.
People engage with information system to perform business processes.
Key components of an Information System
- People: Users and administrators who interact with the system.
- Software: Applications and programs that process and manage data.
- Data: Information that is processed and stored, collected and analyzed.
- Hardware: Physical devices like computers, servers, and networking equipment.
- Processes: Procedures and rules that govern how the system operates.
In essence, an information system is a covering term that integrates all these elements to manage and process information effectively.
Information systems can range from simple, manual paper- or spreadsheet-based solution to complex, automated platforms. Examples include customer databases, payroll systems, inventory management systems, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions. Their primary function is to transform raw data into meaningful insights that support effective decision-making and organizational performance.
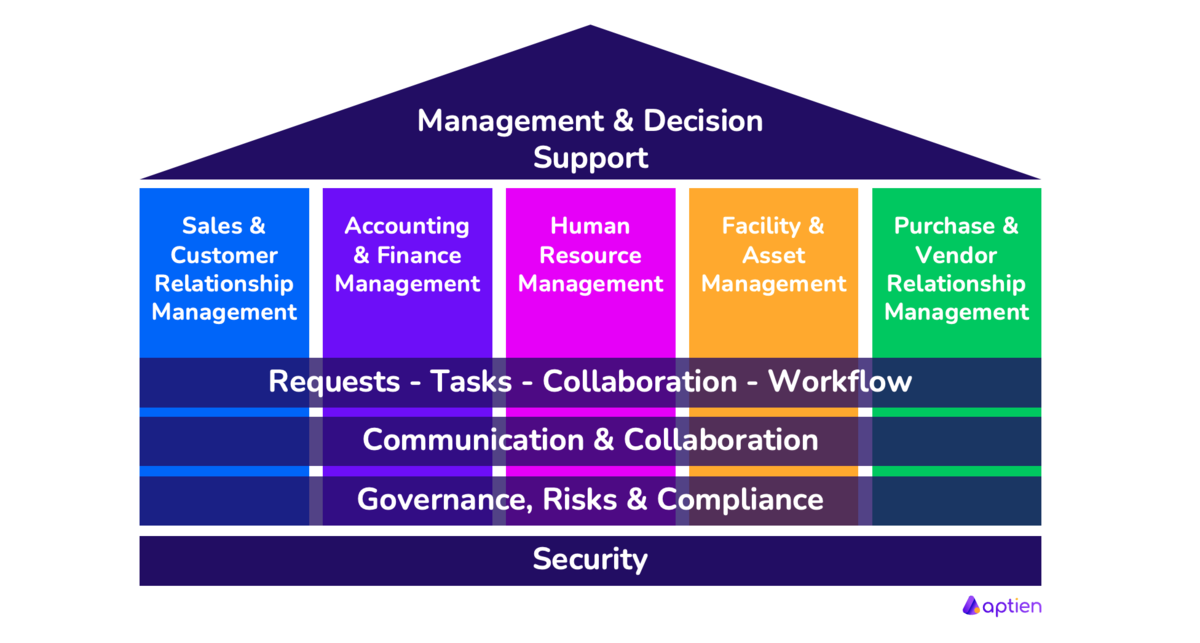
Information system's essential parts and examples
Every single process, task, activity or decision in the organization need some information and therefore must be supported by information technologies. It means either a paper or some kind of business software. This means that any business processes from human resource management, enterprise resource planning, accounting, payroll processing, up to work management should be supported by either any software or a paper. Yes, Let's not forget the most widespread part of information system, the papers. They still carry and contain a large amount of information even in today's digital age.
There is no software covering all processes, information system always consist of several software integrated together. Most common business software categories are:
- Accounting software
- Payroll software
- HRIS system, HCM, (Human resource management)
- ERP systems (Enterprise resource management and planning )
- CRM system (Customer relationship management)
- Vendor management software
- Supply Chain Management System
- Project management software
- Task and work management software
- Systems for cooperation, collaboration, and communication
- Work-flow management systems
In general, software that allows people to work together, share and keep data, collaborate and provides them information.
It doesn't matter where and how the information system applications are operated (in the cloud or on the company's infrastructure, premises). Importantly, they store, process and provide information important to the running and management of the organization. It must therefore support all company processes, both the core ones and all supporting and control processes.