Definition of Encryption
Encryption (cryptography) is the process of converting readable data into an unreadable format for unauthorized participants using an encryption key. Neither a person nor an application can read the data without the key.
Examples of Using Encryption
- Encrypt Files and Data: Protect files and data on your computer or disk.
- Full Disk Encryption: Secure the entire disk or device.
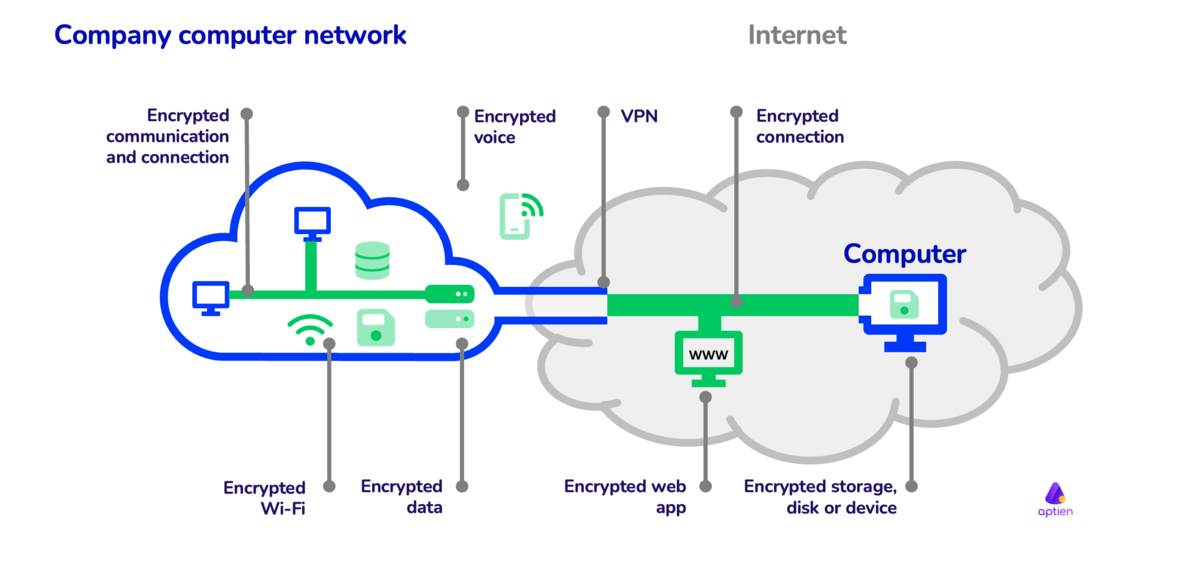
- Encrypted Wi-Fi Connection: Ensure secure wireless communication.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): Provide secure, encrypted internet connections.
- Encrypted Websites: Protect data transmitted between users and websites (e.g., HTTPS).
- Encrypted Voice Communication: Secure voice calls to prevent eavesdropping.
Encryption is an essential cybersecurity measure
Encryption is one of the basic technical measures to protect your data and information. Encryption (cryptography) means that data in readable form is changed to unreadable for unauthorized participants by means of an encryption key. Neither a person nor an application is able to read the data without the key. Encryption is one of the basic cybersecurity measures.
Why and what to encrypt? Why companies use encryption?
Encryption is a way to ensure that only the defined recipient can read the stored data or the sent message or other communication. You only need to encrypt what you need to protect.
- We encrypt stored data so that an unauthorized person cannot read it
- We encrypt communication so that an unauthorized person cannot intercept and listen to it
Nowadays, most communication and data transmission takes place online, using networks and the Internet, so encryption of data transmission, communication or network connection is absolutely necessary and much more important than encryption of stored data.
Using encryption for both storage and communication is strongly recommended by security authorities and standards such as NIST or NIS2.
Encryption as protection of communication and data transfer
Communication encryption is a protection and measure against unauthorized interception of communication or data transmission. For example, it protects data transmission between a website and your computer, or it can protect voice communication between two phones.
- with encryption, the data is unreadable to an attacker who would intercept it
somewhere along the way.
- If you want to be sure that no attacker can read your communications, encryption is essential
Encrypted Wi-Fi connection
- Company Wi-Fi networks are protected by encryption so that no one is allowed
to log in to the network
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- A VPN (virtual private network) protects communications by creating a protected channel (virtual network) between computer and company network
- A VPN is used, for example, to connect from home to the network at work
A website or web app with a security certificate
- encrypted communication is used for web applications and websites. Practically standard nowadays
- communication between your computer and the site or application then takes place securely
- you can recognize a site with encrypted data transmission by its address starting with the letters https or "green line"
Encrypted communication in applications
- most of modern applications today include encryption of data transmission so that communication between the server and the user's device takes place securely
Encrypted email communication
- e-mails are the basic pillars of communication in companies, so e-mail communication should also be subject to encryption and other security. An encrypted digital signature can also be used
- Here, communication is encrypted via SSL/TLS
Encrypted voice communication
- also, the voice telephone transmission can be encrypted, protecting the voice communication against unwanted eavesdropping
Encryption of stored data and individual devices
Data encryption is a protection against unauthorized access to the drive or data. It should be mentioned that data encryption will not protect you when an attacker steals your credentials. In that case, he has the same access to the data as you, regardless of whether the data is encrypted or not
- Encryption of stored data can also be abused, for example ransomware blackmail, where the attacker encrypts your data and you cannot access it
File and data encryption
- You only encrypt selected files or folders, such as a user's profile, credentials, passwords, individual directories or files
- Encrypt selected data, for example passwords
Encrypt the entire disk or device
- full disk encryption secures the entire hard or portable drive, so simply said the entire device is protected
- all information on the disk or device is protected
- if someone steals encrypted disk or device, the data on the disk cannot read or use