Middle Management Explained Simply
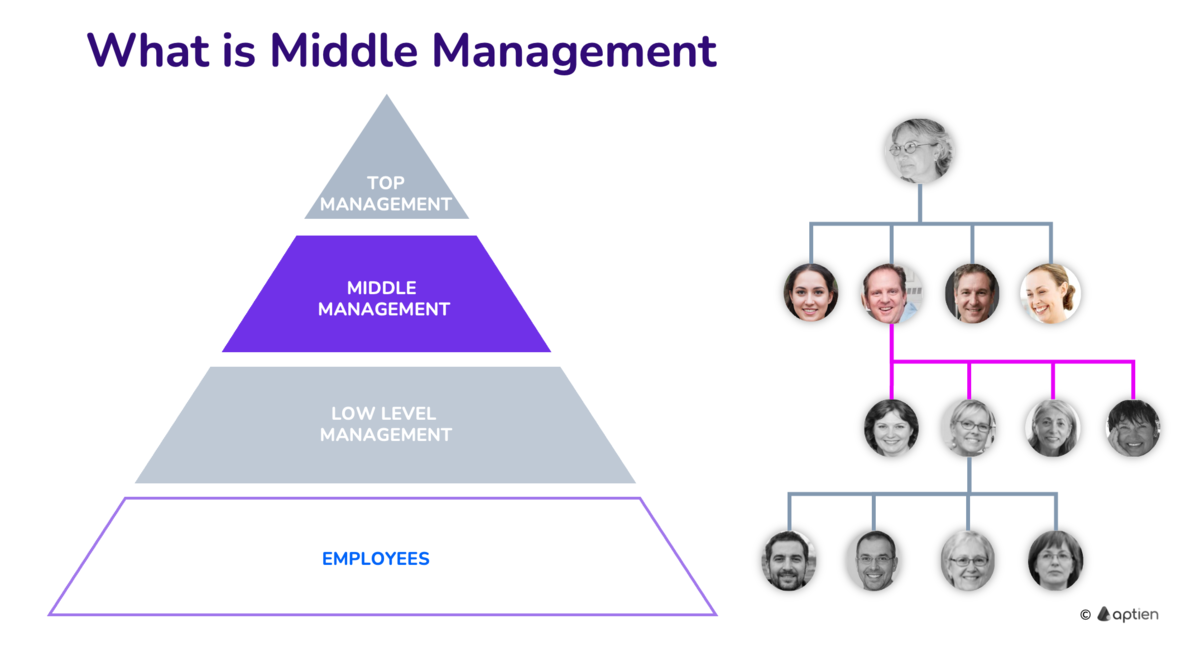
- Middle management are the supervisors and managers who sit between senior leaders (owners, founders, CEO, directors) and frontline staff (production workers, technicians, salespeople, office/admin staff).
- Small and mid-sized businesses commonly add middle managers as they grow—often once the team passes about 15–25 employees—to handle day-to-day coordination, people management, and reporting.
Middle management in small companies (20–50 people)
In a business of this size, middle management is often an informal, hybrid role. These people usually still do their original job while taking on leadership tasks: organizing day-to-day work, assigning tasks, coaching less experienced colleagues, and stepping in for the owner or founder on operational matters. They translate the owner’s or CEO’s priorities into practical actions and bring frontline feedback back to leadership. They handle onboarding, early performance conversations, basic conflict resolution, and help maintain company culture. Frequently they have little or no formal management training but are essential for scaling operations and supporting the team.
Example (small construction company, 25 people):
- Owner / Founder = top management
- Site Manager / Foreman = middle management (directly manages ~10 workers)
- Warehouse Clerk, Accountant = frontline staff
Middle management in medium-sized companies (50–250 people)
At this size, middle management becomes a defined layer. Department heads or managers (operations, production, sales, IT, HR, etc.) sit below senior leadership and oversee supervisors or team leads. They set team targets, plan resources, coordinate between departments, develop people, and report results up to the executive level. Middle managers ensure processes run reliably, handle more complex personnel issues, and implement strategic initiatives at the team level.
Example (manufacturing company, 120 people):
- CEO, CFO = top management
- Production Manager, Logistics Manager, HR Manager = middle management
- Shift Supervisor, Team Lead = front-line supervisors
- Machine Operator, Warehouse Worker = frontline staff
Definition of Mid-Level Manager
A mid-level manager is responsible for overseeing a specific department, division, or functional area within a company. They manage resources, coordinate projects, and lead the teams within their unit. Mid-level managers typically report to senior leadership while also managing and guiding the front-line managers or teams below them. Their primary role is to translate the strategic goals set by senior leadership into practical, operational activities, which are then carried out by the teams under their supervision.
The main functions and tasks of middle management include:
- Translating company-wide strategies into actionable daily operations and processes, ensuring compliance.
- Managing their assigned department, division, or team as a whole.
- Leading and mentoring front-line managers or team leaders within their unit.
- Guiding individual team members in their daily tasks and organizing their workflow.
- Monitoring work progress and checking the quality of team members' outputs.
- Resolving workplace conflicts, clarifying ambiguities, and addressing team challenges.
- Handling day-to-day operational issues and problems as they arise.
Examples of mid-level managers:
- Department Manager or Division Head
- Branch Manager
- Operations Manager
Common Duties and Responsibilities of Mid-Level Management
Mid-level managers handle day-to-day operations at a specific location, team, or department. While senior leaders set company-wide strategy and long-term goals, middle managers focus on managing staff, processes, and daily results. Typical duties for mid-level managers in small and medium-sized businesses include:
- Creating and Running Daily Operations: Setting up and keeping consistent daily routines and workflows for a store, office, shop floor, or team.
- Monitoring Employee Performance: Tracking staff performance, providing feedback, and conducting regular check-ins or reviews.
- Assigning and Supervising Tasks: Delegating work, clarifying responsibilities, and ensuring tasks are completed correctly and on time.
- Ensuring Compliance: Making sure staff follow company policies, safety rules, and any legal or regulatory requirements.
- Motivating and Supporting Staff: Coaching, recognizing good work, and addressing morale or engagement issues to keep teams productive.
- Improving Efficiency and Productivity: Identifying process improvements, reducing bottlenecks, and implementing practical changes that save time and cost.
- Hiring and Retaining Employees: Participating in recruitment, onboarding, training, and creating conditions that help retain reliable employees.
- Turning Strategy into Action: Translating senior leadership’s goals into concrete policies, procedures, and action plans for the team.
- Managing Resources: Allocating staff time, budgets, equipment, and supplies to meet operational needs.
- Reporting Upward: Providing clear updates, performance metrics, problems, and resource requests to senior management.
How You Can Manage Your Team as a Mid-Level Manager in Aptien
As a middle manager, you have direct subordinates set up in the organizational structure. With them, you can:
- Approve Requests: Handle and approve requests from your team members.
- Task Overview: (Feature under construction) Get an overview of your team’s tasks.
- Access Personal Files: View personal files, including personal information, onboarding, adaptation, training, and other development plans.
- Manage Resources: Track issued work equipment, tools, completed training, and other relevant information.
- Organizational Unit Overview: Maintain an overview of all individuals within your organizational unit.