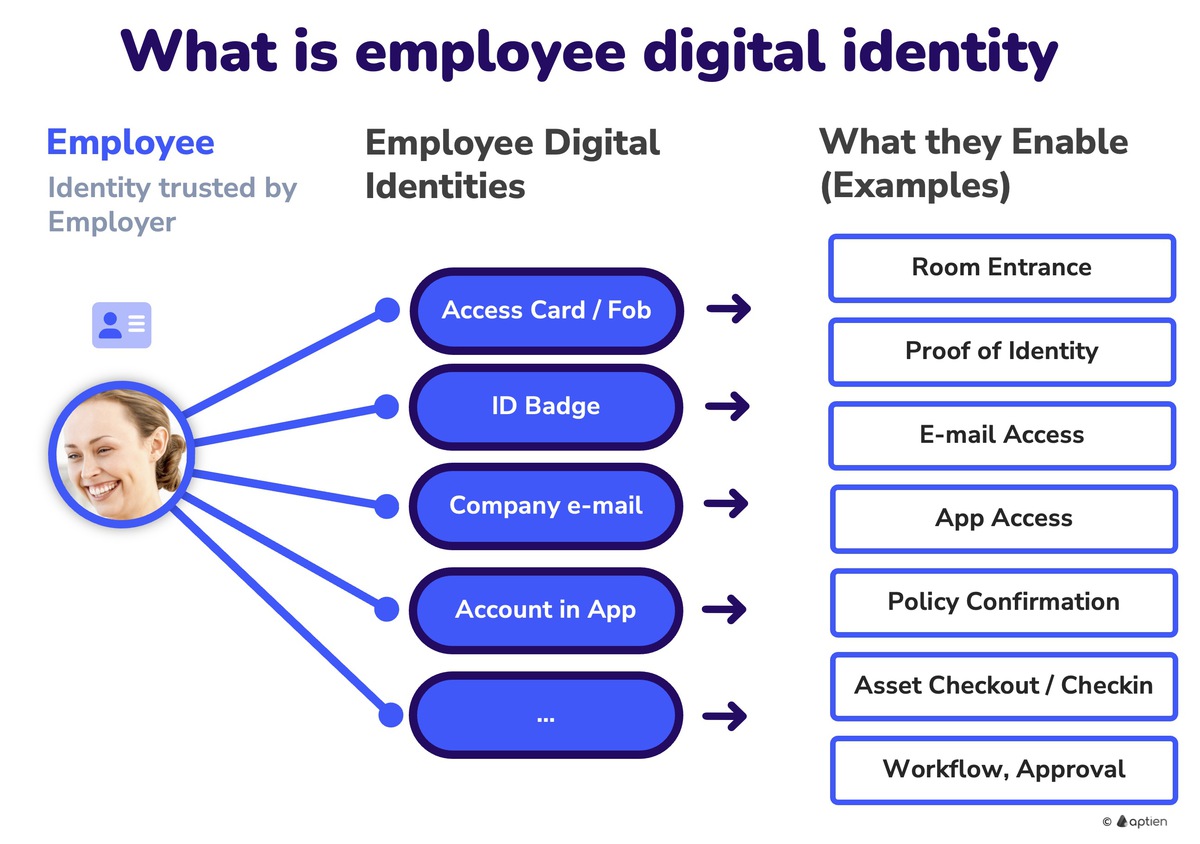
What is an employee digital identity
An employee’s digital identity is the collection of all accounts, access rights, and identifiers the company provides so the employee can work securely and prove they are part of the organization. In practice, the company creates it after in-person identity verification during onboarding (government ID check, signing the employment agreement) and manages it throughout the employee lifecycle (onboarding, role changes, offboarding).
Key components of an employee digital identity
1. User accounts
- Accounts for business systems (e.g., email, accounting, CRM, HR, cloud storage).
- Include a unique ID, role, and permissions (what the user is allowed to do).
- Governed by the principle of least privilege and regular access reviews/audits.
2. Company email
- The most common “face” of the employee’s identity—often used as the username for other apps.
- Serves as a verification channel (password reset, alerts, approvals).
- If compromised, an attacker can impersonate the employee (business email compromise, invoice fraud, resetting other passwords).
3. Access card / badge (employee ID badge)
- The physical form of identity on-site—opens doors and turnstiles; often shows name/photo.
- Linked to the digital identity—the system logs who entered where and when.
- Advantage over keys: a lost card can be deactivated immediately.
Why Employee Identity Matters for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
For SMBs, employee identity is critical for simplifying access, strengthening security, and automating HR processes.In practice, it helps to:
- Simplify access to company tools — employees use a single account to sign in to all apps (SSO — Single Sign-On).
- Manage workflows — submitting requests and approvals
- Track handover of work equipment and other confirmations
- Increase data security — identity verification (e.g., MFA — Multi-Factor Authentication) reduces the risk of account misuse.
- Secure physical access to offices and facilities
- Streamline onboarding and offboarding — when an employee joins, their digital identity is created and access is provisioned automatically; when they leave, everything is deprovisioned.
How to protect employee digital identity in a small or mid-sized business
- Keep clear visibility: track who has access to which systems, apps, and data
- Onboarding: Provision accounts using a checklist aligned to the employee’s role; set least-privilege access from day one
- Offboarding: Deprovision and disable all accounts on the employee’s last day using a checklist. Leaving access active for company accounts, SaaS apps, Wi‑Fi, or email is a security risk
- Enforce a password policy: Require strong, unique passwords and a password manager; do not share passwords; follow basic cyber hygiene
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)—grant access based on job role and responsibilities, and conduct regular access reviews