Access Control means technologies and methods that restrict people's access to buildings, rooms, IT systems, or data so that only those who are authorized can reach them.
Why Is Access Control Important for Small and Growing Businesses?
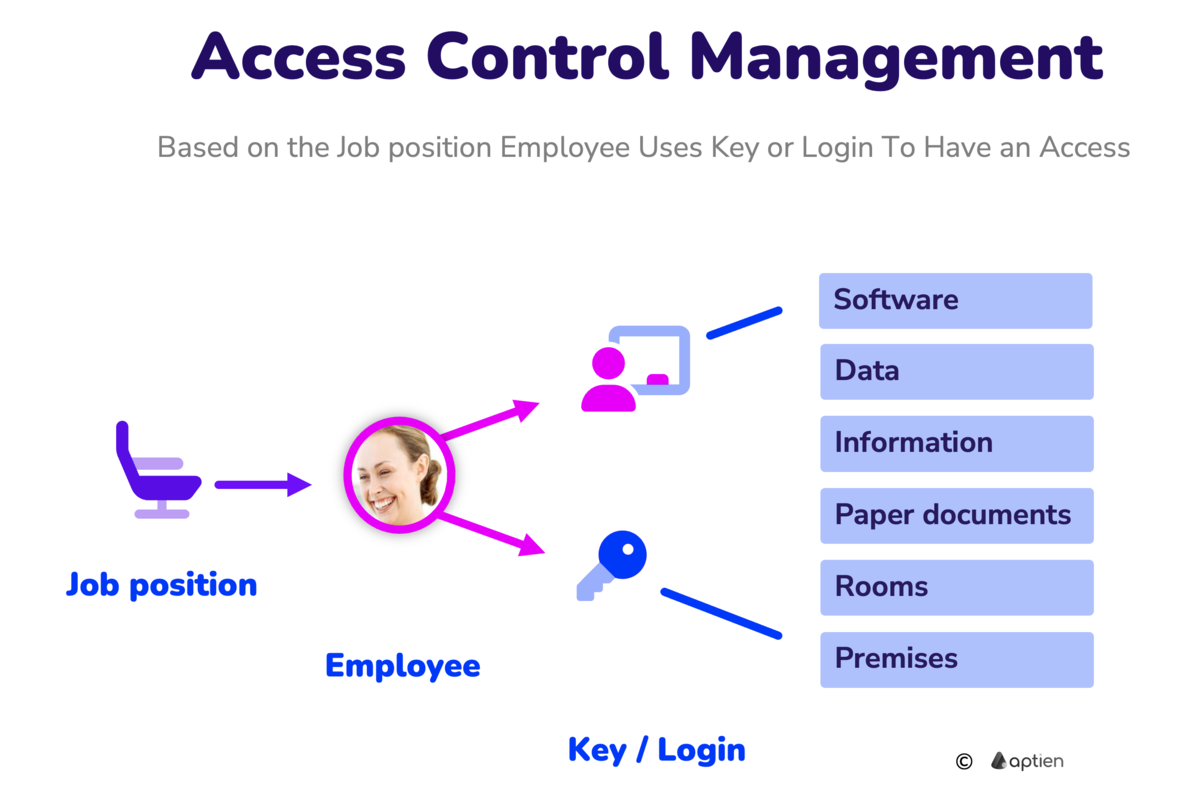
Access control means managing who can access which resources. Simply put, it helps your business decide who can enter your physical spaces like your office or warehouse, and who can use your digital tools such as software, business systems, and applications. This can be handled with things like physical keys, access cards, passwords, or digital user accounts.
Why is Access Management Important for SMBs?
- Protects assets and sensitive data.
- Ensures the safety of people.
- Is a key part of employee onboarding and offboarding.
How Can Aptien Help You Manage Access?
- Keep track of who has which key or access card, when they received it, and when they returned it.
- Help onboard new employees by managing what they need and setting up their access permissions.
- Quickly identify which access rights need to be disabled when an employee leaves.
- Manage login credentials, user accounts, software licenses, and access to IT systems.
While Aptien doesn’t directly control your locks or security hardware, it helps you monitor who has been issued access cards or passwords, making it easier to manage who can enter specific areas.
- Learn how to organize keys, cards, and employee access
- Learn how to define employee permissions in job descriptions
- Try Aptien and take control of access management in your business.